Comparison of abdominal pain and distention due to insufflation with CO2 versus insufflation with air in an advanced digestive endoscopy unit in Manizales, Colombia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.340Keywords:
Colonoscopy, carbon dioxide, endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, air, abdominal circumference, painAbstract
Objective: This study compares the incidence of abdominal pain and distension, the magnitude of pain, abdominal perimeter, and related complications related to two different insufflating agents.
Patients and Method: Prospective analytical cohort study. Data were collected from 43 performances of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCPs) and 20 colonoscopies in which patients were insufflated with CO2. A control examination using ambient air for insufflation was performed for each patient. In total, 86 ERCPs and 40 colonoscopies were performed. The study includes clinical characterizations, bivariate analysis and multivariate analysis.
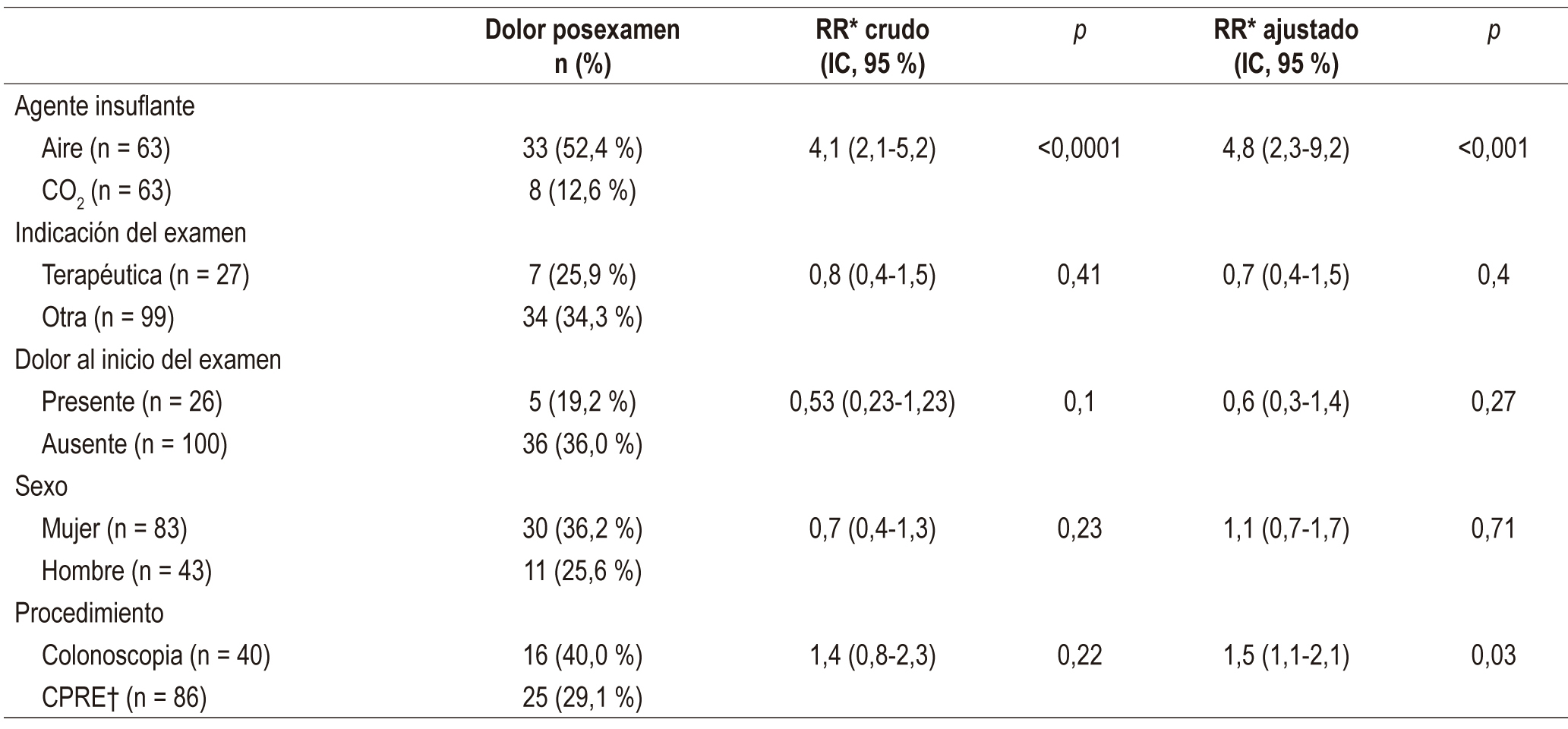
Results: The most painful procedure was colonoscopy, but 60% of colonoscopy patients and 70% of ERCP patients had no pain 15 minutes after waking up following their examinations. No statistically significant differences related to reasons for examination, presence or intensity of pain at the time of the procedure, age, sex or diagnosis were found. The relative risk (RR) of immediate pain is 4.8 times higher when insufflation is done with air instead of CO2 (RR = 4.8; 95% CI: 2.3 to 9.2; p <0.001). The risk of abdominal distension in the air group was 2.6 times higher than that of the group insufflated with CO2 (RR = 2.6; 95% CI: 1.8 to 3.9; p <0.001). CO2 reduces the likelihood and extent of abdominal distension and immediate post colonoscopy or ERCP pain. There were no complications in any of the 126 patients.
Conclusions: Abdominal pain and bloating occur less frequently and less intensely when CO2 is used as an insufflating agent. None of the procedures presented major complications.
Downloads
References
De-Quadros LG, Kaiser-Júnior RL, Felix VN, Villar L, Campos JM, Nogueira VQ, et al. Colonoscopy: randomized comparative study of insufflation with carbon dioxide versus air. Arq Bras Cir Dig. 2017;30(3):177–181. https://doi.org/10.1590/0102-6720201700030004
Kim HG. Painless Colonoscopy: Available Techniques and Instruments. Clin Endosc. 2016;49(5):444–448. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2016.132
Chen SW, Hui CK, Chang JJ, Lee TS, Chan SC, Chien CH, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy can significantly decrease post-interventional abdominal discomfort in deeply sedated patients: A prospective, randomized, double-blinded, controlled trial. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;31(4):808-13. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.13181
Hsu WF, Hu WH, Chen YN, Lai HH, Chen MK, Chang LC, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation can significantly reduce toilet use after colonoscopy: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. 2014;46(3):190-5. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1365016
Falt P, Šmajstrla V, Fojtík P, Hill M, Urban O. Carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy in inflammatory bowel disease patients: a double-blind, randomized, single-center trial. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;29(3):355-359. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000000791
Kiriyama S, Naitoh H, Fukuchi M, Yuasa K, Horiuchi K, Fukasawa T, et al. Evaluation of abdominal circumference and salivary amylase activities after unsedated colonoscopy using carbon dioxide and air insufflations. J Dig Dis. 2015;16(12):747-51. https://doi.org/10.1111/1751-2980.12302
Sajid MS, Caswell J, Bhatti MI, Sains P, Baig MK, Miles WF. Carbon dioxide insufflation vs conventional air insufflation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis of published randomized controlled trials. Colorectal Dis. 2015;17(2):111-23. https://doi.org/10.1111/codi.12837
Cotton PB. Fifty years of ERCP: a personal review. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018;88(2):393-396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2018.04.013
Memon MA, Memon B, Yunus RM, Khan S. Carbon Dioxide Versus Air Insufflation for Elective Colonoscopy: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 2016;26(2):102-16. https://doi.org/10.1097/SLE.0000000000000243
Zhang WY, Jiang XP, Miao L, Chen FC, Huang ZM, Huang XL. Efficacy and safety of carbon dioxide insufflation versus air insufflation for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A meta-analysis update. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2017;41(2):217-229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2016.10.001
Muraki T, Arakura N, Kodama R, Yoneda S, Maruyama M, Itou T, et al. Comparison of carbon dioxide and air insufflation use by non-expert endoscopists during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Dig Endosc. 2013;25(2):189-96. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1443-1661.2012.01344.x
Shi H, Chen S, Swar G, Wang Y, Ying M. Carbon dioxide insufflation during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: a review and meta-analysis. Pancreas. 2013;42(7):1093-100. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0b013e3182909da5
Greenland S. Modeling and variable selection in epidemiologic analysis. Am J Public Health. 1989;79(3):340-9. https://doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.79.3.340
Kovalchik SA, Varadhan R, Fetterman B, Poitras NE, Wacholder S, Katki HA. A general binomial regression model to estimate standardized risk differences from binary response data. Stat Med. 2013;32(5):808-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.5553
McInturff P, Johnson WO, Cowling D, Gardner IA. Modelling risk when binary outcomes are subject to error. Stat Med. 2004;23(7):1095-109. https://doi.org/10.1002/sim.1656
Ministerio de Salud de la República de Colombia. Resolución número 8430 de 1993: por la cual se establecen las normas científicas, técnicas y administrativas para la investigación en salud. Bogotá; 1993.
Lolas F. Aspectos éticos de la investigación biomédica. Conceptos frecuentes en las normas escritas. Rev Med Chile. 2001;129(6):680-684. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0034-98872001000600014
Liu X, Liu D, Li J, Ou D, Zhou Z. Safety and efficacy of carbon dioxide insufflation during colonoscopy. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009;34(8):825-9.
Díez-Redondo P, Gil-Simón P, Alcaide-Suárez N, Atienza-Sánchez R, Barrio-Andrés J, De-la-Serna-Higuera C, et al. Comparison between insufflation with air or carbon dioxide during the colonoscopy in sedated patients with propofol. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2012;104(8):411-7. https://doi.org/10.4321/S1130-01082012000800004
Cheng Y, Xiong XZ, Wu SJ, Lu J, Lin YX, Cheng NS, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation for endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography: A meta-analysis and systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18(39):5622-31. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v18.i39.5622
Ibáñez J, Vanaclocha-Espí M, Pérez Sanz E, Valverde MJ, Sáez-Lloret I, Barceló AM, et al. Complicaciones graves en las colonoscopias de cribado del cáncer colorrectal en la Comunidad Valenciana. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;41(9):553:561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastre.2018.11.008
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, Niro G, Valvano MR, Spirito F, et al. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(8):1781-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01279.x
Katsinelos P, Lazaraki G, Chatzimavroudis G, Gkagkalis S, Vasiliadis I, Papaeuthimiou A, et al. Risk factors for therapeutic ERCP-related complications: an analysis of 2,715 cases performed by a single endoscopist. Ann Gastroenterol. 2014;27(1):65–72.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |















