Diagnosis of Celiac Disease after Starting Antitubercular Medication: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.986Keywords:
Celiac Disease, Tuberculosis, Triticum, Excipients, Case ReportAbstract
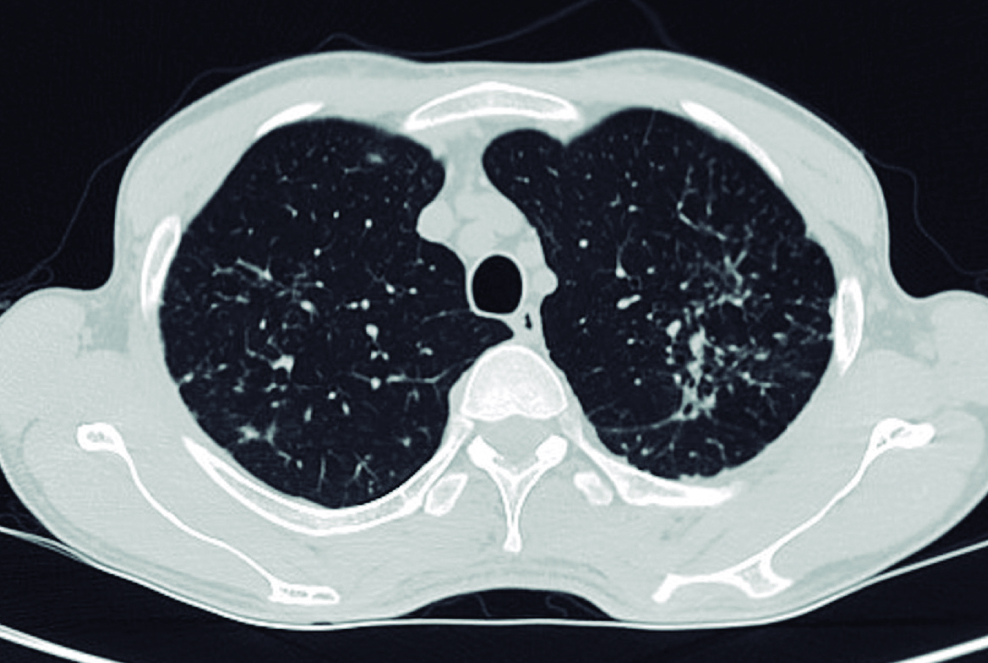
We present the case of a young patient from Argentina living in a rural area without any relevant medical history. He consulted the emergency department after blunt chest trauma, and during trauma studies, images compatible with pulmonary tuberculosis were found, a diagnosis made incidentally.
After starting treatment, he exhibited gastrointestinal symptoms such as diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss, which were initially considered an adverse effect of treatment with rifampin/isoniazid/pyrazinamide/ethambutol (RHZE). Upon completing the first phase of treatment and suspending the medication, the symptoms improved, and the bacilloscopies were negative.
Subsequently, the severity of the symptoms drew attention. Additional paraclinical tests were performed with malabsorptive diarrhea results, considering the patient’s origin and the fact that his diet included products that he grew himself without prior exposure to gluten. Celiac disease is suspected, and antibodies and biopsy results compatible with this entity were obtained. When reviewing the association of symptom onset with the RHZE/pyridoxine treatment, we found these medications may have wheat-based excipients, which explains the worsening of symptoms, not due to the gastrointestinal adverse effects of the antibiotic but its excipients.
Finally, the case was analyzed, tuberculosis was ruled out, and treatment was suspended, refocusing the therapeutic effort on recovering the patient’s nutritional status. Subsequently, no other hospital admissions were recorded, and he remained respiratorily asymptomatic, with weight gain and nutritional recovery.
Downloads
References
Singh P, Arora A, Strand TA, Leffler DA, Catassi C, Green PH, et al. Global Prevalence of Celiac Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(6):823-36.e2. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2017.06.037
King JA, Jeong J, Underwood FE, Quan J, Panaccione N, Windsor JW, et al. Incidence of Celiac Disease Is Increasing over Time: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(4):507-25. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000523
Parra-Medina R, Molano-Gonzalez N, Rojas-Villarraga A, Agmon-Levin N, Arango MT, Shoenfeld Y, et al. Prevalence of celiac disease in Latin America: A systematic review and meta-regression. PLoS One. 2015;10(5):e0124040. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0124040
Suarez-Correa J, López-Barreto JC, Mejía-Cardona AF, Paredes-Fernández AJ. Enfermedad celíaca: un reto diagnóstico en Colombia. Repert. Med. Cir. 2022;31(2):123-32. https://doi.org/10.31260/RepertMedCir.01217372.1159
Dickson BC, Streutker CJ, Chetty R. Coeliac disease: an update for pathologists. J Clin Pathol. 2006;59(10):1008-16. https://doi.org/10.1136/jcp.2005.035345
Cerezo-Lajas A, Caminero-Luna JA, Rodríguez-Guzmán MC, Miguel-Díez J. Tratamiento antituberculoso en un paciente con enfermedad celíaca. Archivos de Bronconeumologia. 2018;54(6):337-38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arbres.2017.12.009
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















