Educational models for learning Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) and Endoscopic Ultrasound Elastography
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.454Keywords:
POEM, elastography, endoscopic ultrasound, achalasia, cystic lesions, solid tumorsAbstract
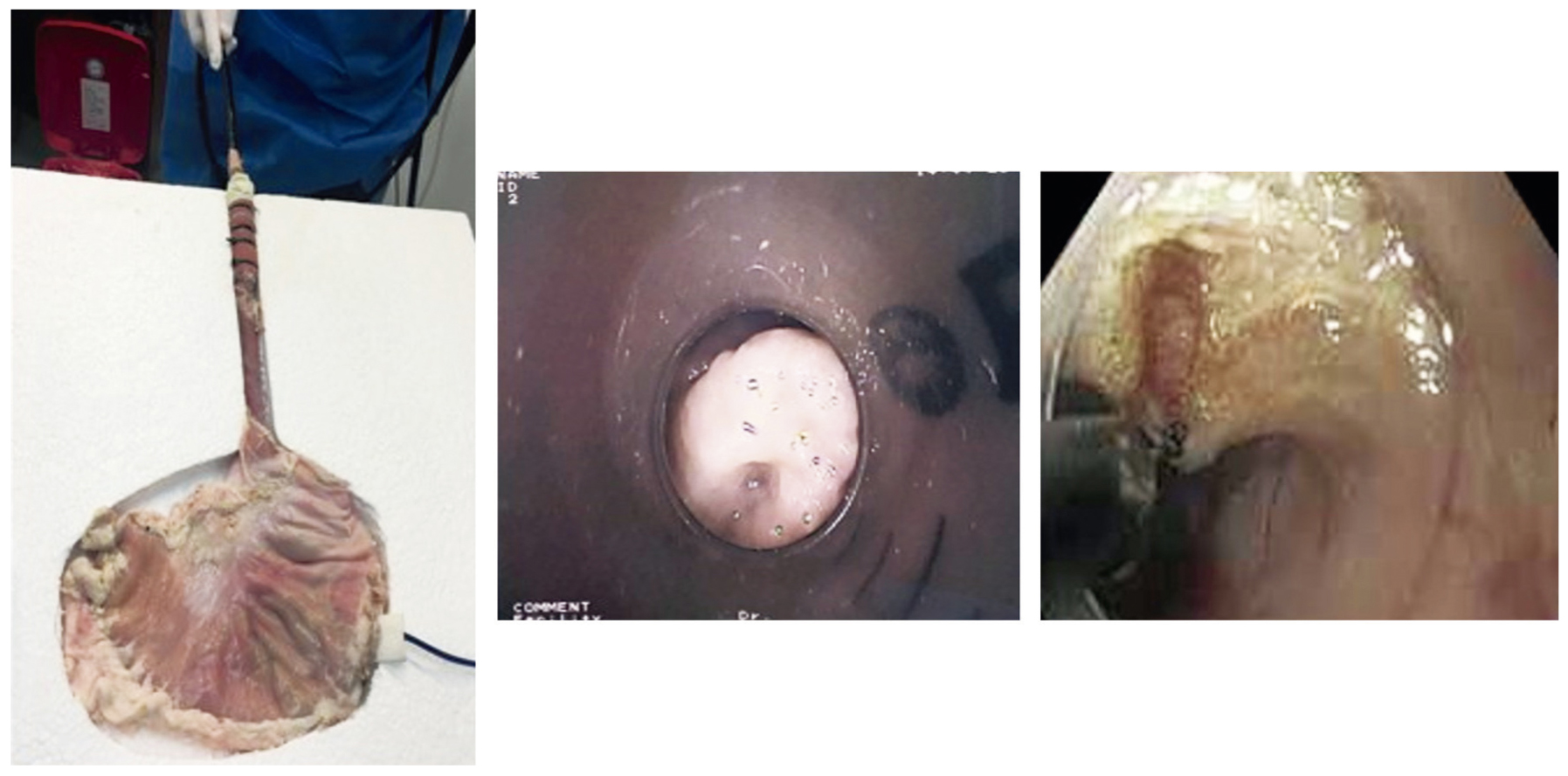
Objectives: This article presents the development of educational models for learning two widespread recent endoscopic techniques which have great clinical implications. Its sole intention is to allow acquisition of basic and advanced skills by residents and gastroenterologists.
Materials and methods: Two simple, very low cost, easily reproducible and reusable models were devised. Procedures are fully described in ways that allow the operator to integrate the development of skills and acquisition of the minimum theoretical concepts required without the pressures generated by risks of complications.
Results: The current global trend is to develop teaching models that accelerate the learning curve for highly demanding procedures that are associated with potentially serious complications. With these models it is possible to test endoscopists through continuous supervised evaluations. Implementation by gastroenterology units can be done easily without the need for large investments or travel to other countries.
Conclusions: This is a great contribution to the scientific and educational development of Colombia since neither development of new endoscopic techniques nor the process of learning how to perform them should put patients at risk. We agree with the ideas of numerous medical associations regarding theoretical-practical courses of short duration even though some virtual sessions, “do not constitute the minimum training required needed for accreditation.
Downloads
References
Bisschops R, Wilmer A, Tack J. A survey on gastroenterology training in Europe. Gut. 2002;50(5):724-9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gut.50.5.724
McCashland T, Brand R, Lyden E, de Garmo P. The time and financial impact of training fellows in endoscopy. CORI Research Project. Clinical Outcomes Research Initiative. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95(11):3129-32. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03280.x
Bini EJ, Firoozi B, Choung RJ, Ali EM, Osman M, Weinshel EH. Systematic evaluation of complications related to endoscopy in a training setting: A prospective 30-day outcomes study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;57(1):8-16. https://doi.org/10.1067/mge.2003.15
Cohen J, Thompson CC. The next generation of endoscopic simulation. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013 Jul;108(7):1036-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2012.390
Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Wilcox M. 298 Endoscopic Transmural Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections (PFCs) in 200 Consecutive Patients: An Assessment of Outcomes. 2011;73(4):AB122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2011.03.038
AbouHashem Y, Dayal M, Savanah S, Štrkalj G. The application of 3D printing in anatomy education. Med Educ Online. 2015;20:29847. https://doi.org/10.3402/meo.v20.29847
Eleftheriadis N, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Onimaru M, Maselli R, Santi G. Submucosal tunnel endoscopy: Peroral endoscopic myotomy and peroral endoscopic tumor resection. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2016;8(2):86–103. https://doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v8.i2.86
Li QL, Zhou PH. Perspective on peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia: Zhongshan experience. Gut Liver. 2015;9(2):152-8. https://doi.org/10.5009/gnl14227
Onimaru M, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Sato C, Sato H, Phalanusitthepha C, et al. Greater curvature myotomy is a safe and effective modified technique in per-oral endoscopic myotomy (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(6):1370-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2014.11.014
Onimaru M, Inoue H, Ikeda H, Yoshida A, Santi EG, Sato H, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy is a viable option for failed surgical esophagocardiomyotomy instead of redo surgical Heller myotomy: a single center prospective study. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217(4):598-605. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.05.025
Eleftheriadis N, Protopapas A, Katsogridakis J, Hatzitolios AI. Successful peroral endoscopic myotomy for radical treatment of sigmoid-type esophageal achalasia by Greek gastroenterologists. Ann Gastroenterol. 2014;27(4):430–431.
Li QL, Chen WF, Zhou PH, Yao LQ, Xu MD, Hu JW, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a clinical comparative study of endoscopic full-thickness and circular muscle myotomy. J Am Coll Surg. 2013;217(3):442-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2013.04.033
Sedlack RE, Kolars JC. Computer simulator training enhances the competency of gastroenterology fellows at colonoscopy: results of a pilot study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(1):33-7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04007.x
Gómez MA. Utilidad de un modelo para el entrenamiento del ultrasonido endoscópico radial y lineal. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2007;22:104-110.
Nightingale K, Bentley R, Trahey G. Observations of tissue response to acoustic radiation force: opportunities for imaging. Ultrason Imaging. 2002;24(3):129-38. https://doi.org/10.1177/016173460202400301
Grimes KL, Inoue H. Per Oral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: A Detailed Description of the Technique and Review of the Literature. Thorac Surg Clin. 2016;26(2):147-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.thorsurg.2015.12.003
Nightingale K, McAleavey S, Trahey G. Shear-wave generation using acoustic radiation force: in vivo and ex vivo results. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003;29(12):1715-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.08.008
Bercoff J, Tanter M, Fink M. Supersonic shear imaging: a new technique for soft tissue elasticity mapping. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2004;51(4):396-409. https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2004.1295425
Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, Beaugrand M, Palau R. Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2003;29(12):1705-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2003.07.001
Sandrin L, Tanter M, Catheline S, Fink M. Shear modulus imaging with 2-D transient elastography. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2002;49(4):426-35. https://doi.org/10.1109/58.996560
Harewood GC, Wiersema MJ, Nelson H, Maccarty RL, Olson JE, Clain JE, et al. A prospective, blinded assessment of the impact of preoperative staging on the management of rectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(1):24-32. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.34163
Chang KJ, Nguyen P, Erickson RA, Durbin TE, Katz KD. The clinical utility of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration in the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic carcinoma. Gastrointest Endosc. 1997;45(5):387-93. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5107(97)70149-4
Hochberger J, Maiss J, Magdeburg B, Cohen J, Hahn EG. Training simulators and education in gastrointestinal endoscopy: current status and perspectives in 2001. Endoscopy. 2001;33(6):541-9. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-14972
Silver B, Metzger TS, Matalon TA. A simple phantom for learning needle placement for sonographically guided biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1990;154(4):847-8. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.154.4.2107686
Burmester E, Leineweber T, Hacker S, Tiede U, Hütteroth TH, Höhne KH. EUS Meets Voxel-Man: three-dimensional anatomic animation of linear-array endoscopic ultrasound images. Endoscopy. 2004;36(8):726-30. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-825669
Fusaroli P, Caletti G. Endoscopic ultrasonography. Endoscopy. 2003;35(2):127-35. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2003-37010
Classen M, Ruppin H. Practical Endoscopy Training Using a New Gastrointestinal Phantom. Endoscopy 6 (1974) 127-131. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0028-1098609
Qiao W, Bai Y, Lv R, Zhang W, Chen Y, Lei S, et al. The effect of virtual endoscopy simulator training on novices: a systematic review. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e89224. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0089224
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |















