Warthin–Starry stain identification of Helicobacter pylori in biopsies of patients who previously tested negative in hematoxylin-eosin staining for follicular gastritis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.268Keywords:
Chronic gastritis, folicular hyperplasia, Helicobacter pylori, Hematoxylin-Eosin, Warthin-StarryAbstract
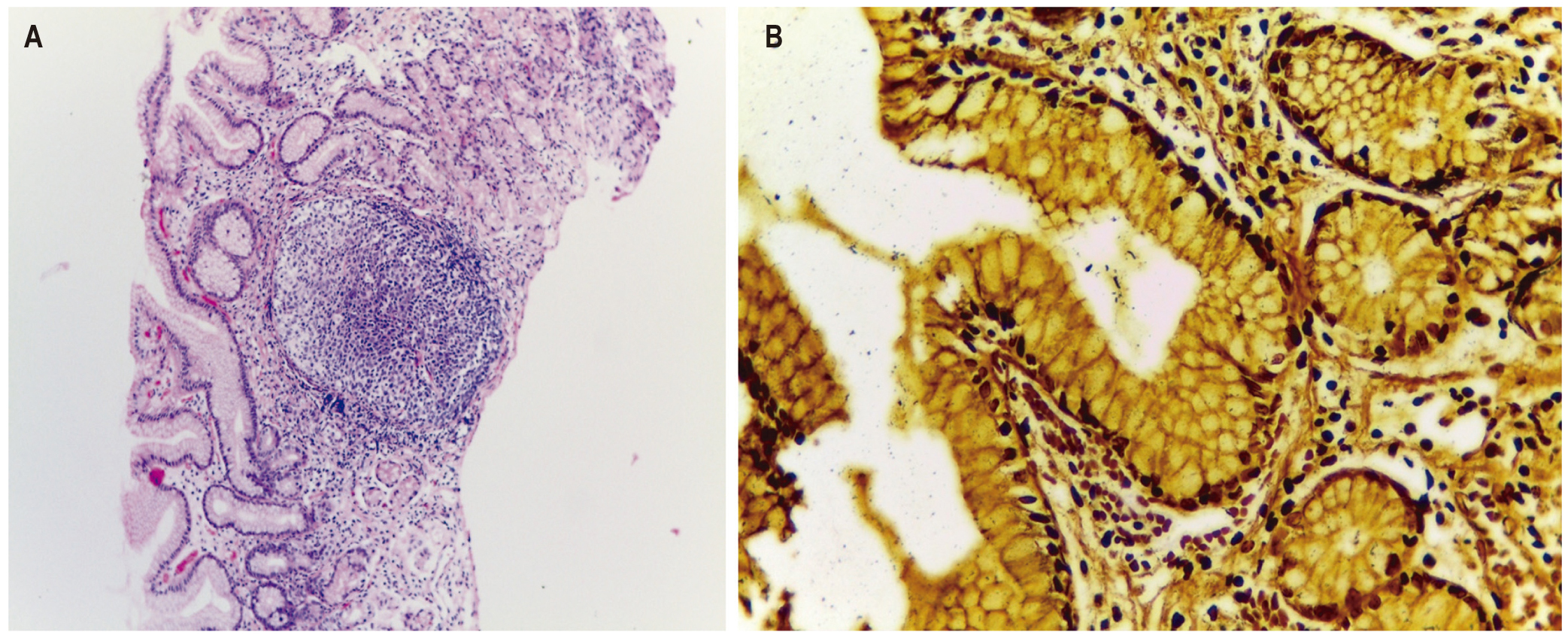
Non-invasive and invasive techniques can be used for detection of Helicobacter pylori. An invasive technique identifies the bacteria through routine hematoxylin-eosin staining. Warthin-Starry stain is rarely used. Objective: Our objective was to identify H. pylori by Warthin-Starry staining of patient’s biopsies with chronic follicular gastritis who had previously tested negative in hematoxylin-eosin staining.
Materials and methods: This is a descriptive, cross-sectional descriptive study that was carried out over a period of 12 months. The study examined paraffin blocks of samples taken from the gastric mucosa of patients diagnosed with chronic gastritis and follicular hyperplasia. A histological section was extracted from a block and tested with hematoxylin-eosin staining for the presence or absence of H. pylori. If absent, an additional cut was taken from the same block and Warthin-Starry staining was used to retest for the presence of the bacteria.
Results: Of the 314 samples collected, 209 tested negative, and 105 tested positive for H. pylori when hematoxylin-eosin staining was used. Of the 209 negative samples, 45% (94) tested positive when Warthin Starry stain was used, and 55% (115) still tested negative.
Conclusion: Findings of H. pylori are significantly higher when Warthin Starry stain was used to test samples whose previous histological study had evidenced an absence of the bacillus, especially in samples with a small amount of bacteria.
Downloads
References
Correa S, Cardona AF, Correa T, Correa LA, García HI, Estrada S. Prevalencia de Helicobacter pylori y características histopatológicas en biopsias gástricas de pacientes con síntomas dispépticos en un centro de referencia de Medellín. Rev Col Gastroenterol. 2016;31(1):9-15. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.67
Buriticá VJ, Becerra LF, Salazar A. Enfermedad ácido péptica. Arch Med Univ Manizales Fac Med. 2005;11:46-55. https://doi.org/10.30554/archmed.11.0.1534.2005
Makola D, Peura DA, Crowe SE. Helicobacter pylori infection and related gastrointestinal diseases. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2007;41(6):548-58. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e318030e3c3
Garg B, Sandhu V, Sood N, Sood A, Malhotra V. Histopathological analysis of chronic gastritis and correlation of pathological features with each other and with endoscopic findings. Pol J Pathol. 2012;63(3):172-8. https://doi.org/10.5114/pjp.2012.31501
Ramírez A, Sánchez R. Helicobacter Pylori y Cáncer Gástrico. Rev Gastroenterol Perú. 2008;28:258-266.
Martínez JD, Riveros SC. Hiperplasia linfoide folicular gástrica e infección por Helicobacter pylori en adultos colombianos. 2009;24(2):148-156.
Camargo MC, Yepez MC, Cerón C, Guerrero N, Bravo LE, Correa P, et al. Age at acquisition of Helicobacter pylori infection: comparison of two areas with contrasting risk of gastric cancer. Helicobacter. 2004;9(3):262-70. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1083-4389.2004.00221.x
Alba RS, Toledo RA, Viana ML. Helicobacter pylori: Clínica, diagnóstico y tratamiento. Rev Posgrado VIa Cátedra Med. 2006;158:9-12.
Marín R, Salas P, Mena F, Sierra R. Identificación histológica de Helicobacter pylori por los métodos de tinción de Warthins-Stary y Giménez en biopsias gástricas. Rev Med Costa Rica Centroam. 1996;53(537):147-151.
Fallone CA, Loo VG, Lough J, Barkun AN. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of gastric tissue for the detection of Helicobacter pylori. Helicobacter. 1997;2(1):32-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-5378.1997.tb00054.x
Prophet EB, Mills B, Arrington J, Sobón L. Métodos histotecnológicos. Washington: Registro de Patología de los Estados Unidos de América (ARP) e Instituto de Patología de las Fuerzas Armadas de los Estados Unidos de América (AFIP);1995.
Campuzano G. Helicobacter Pylori: de la gastritis al cáncer gástrico. Medellín: Editora Médica Colombiana S.A., 8ª edición; 2017.
Kit de plateado según Warthin-Starry modificado para la detección de Helicobacter pylori y Spirochaetes en cortes parafínicos. Burlington: EMD Millipore Corporation; 2019.
Giugni MC, Benmelej A, Graciani G, Gómez JM, Roldán JN, Costamagna A, et al. Comparación de coloraciones histológicas para el diagnóstico de Helicobacter Pylori. Rev FABICIB. 1998;2(1):151-155. https://doi.org/10.14409/fabicib.v2i1.611
Joachín ID, Mendoza AG, Salazar JL. Valor diagnóstico de la tinción de Warthin Starry para la identificación de H. pylori en biopsias gástricas. Guatemala: Universidad de San Carlos de Guatemala, Facultad de Ciencias Químicas y Farmacia; 2016.
Amores J, Arredondo A, Martínez B, Estrada Y, Pereira L, Potente A. Correlación histologicamicrobiológica en el diagnóstico de Helicobacter pylori. Rev Mex Patol Clin. 2010;57(3):135-142.
Ortiz-Martínez MA, Salazar-Valdez OR, Brito-Zurita OR, Abundis-Castro L, García-Bajeca C, Gutiérrez-López SJ, et al. Detección de Helicobacter pylori en niños con los métodos de Gram, Giemsa y Warthing-Starry, inicialmente negativos con otras técnicas histológicas. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2005;70(2):143-145.
Vela-Velásquez CT. Comparación entre las biopsias gástricas sin fijar 24 horas frente a la biopsia convencional para el diagnóstico de Helicobacter pylori en un hospital de referencia de Perú. Rev Perú Med Exp Salud Pública. 2011;28(1):42-46. https://doi.org/10.17843/rpmesp.2011.281.454
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.

| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |
















