Clinical and histopathologic characterization of children with autoimmune hepatitis in a reference center of Bogotá, Colombia
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.346Keywords:
autoimmune hepatitis, child, biopsy, pathologyAbstract
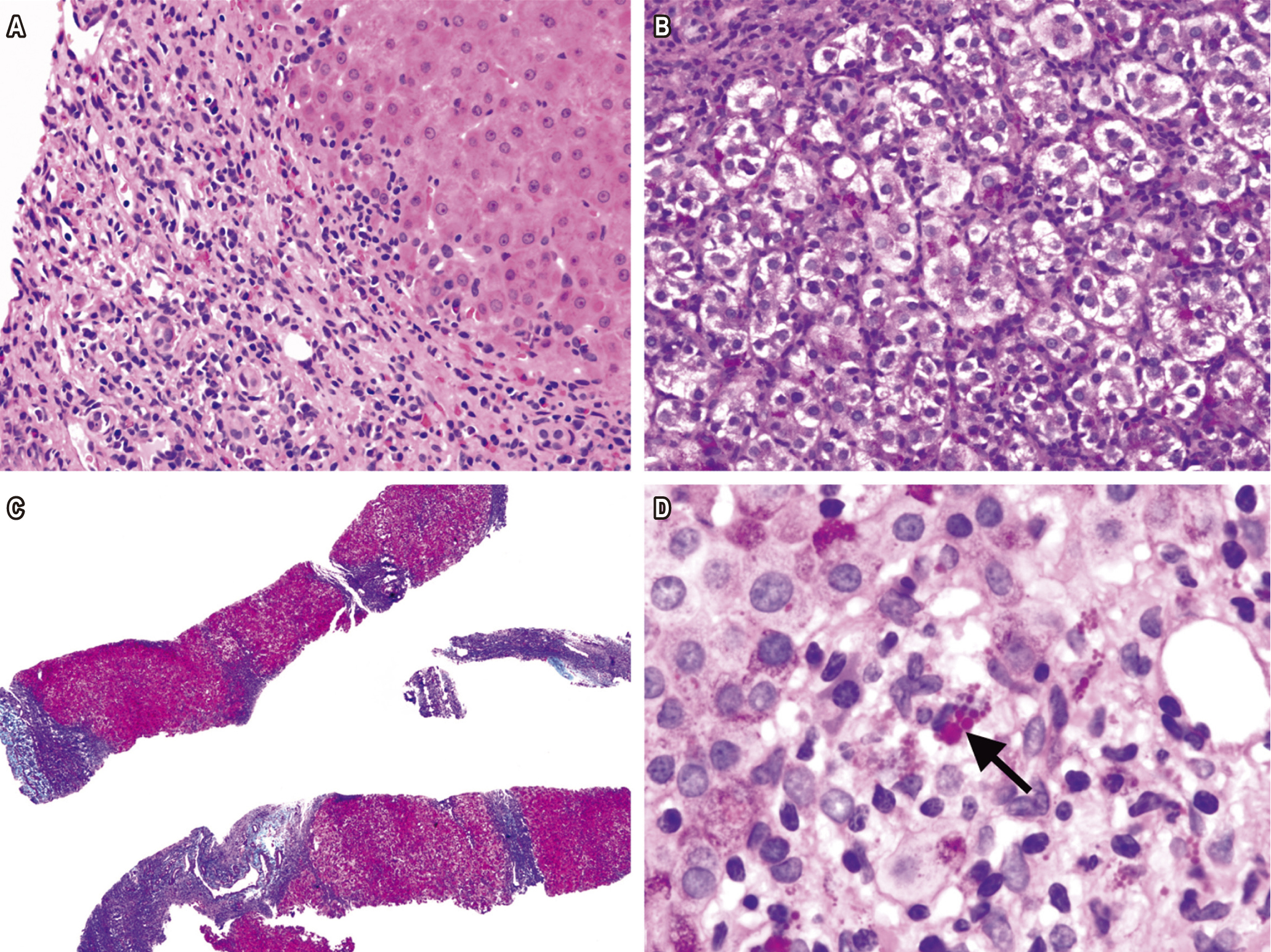
Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a progressive inflammatory liver disease. It is uncommon in children and adolescents, and is a diagnostic challenge for clinicians and pathologists. We describe the clinical, biochemical and histopathological characteristics of 21 pediatric patients with AIH diagnosed in the last 14 years. Liver biopsies were reassessed to analyze histopathological findings in detail. Of the 21 cases evaluated, 12 (57.1%) were girls and young women, the median age was 14 years old, and 17 (80.9%) had type 1 AIH. The most frequent clinical signs were jaundice (66.7%), choluria (44.4%), evidence of portal hypertension with esophageal varices (47.1%), and splenomegaly (41.2%). Histories of other autoimmune diseases were found in 11.8% of these patients. Elevated levels of aminotransferases were found in 89.5% of the patients, hyperbilirubinemia was found in 88.9%, and 60.0% of the cases had low levels of serum albumin. Reassessed biopsies showed portal lymphoplasmocytic infiltrate (94.4%), interface hepatitis (77.8%) and rosette formation (50.0%). Hyaline inclusions were found in Kupffer cells in 42.9% of the biopsies. About 33.5% of the cases showed cirrhosis at the initial biopsy. Despite immunosuppressive treatment, four patients required liver transplantation and two are on the waiting list. AIH in children can manifest with jaundice, choluria, signs of portal hypertension, elevated aminotransferases, hyperbilirubinemia and circulating antibodies. Hyaline inclusions in Kupffer cells may be a useful finding in the histopathological diagnosis of AIH in children.
Downloads
References
Wang Q, Yang F, Miao Q, Krawitt E, Gershwin M, Ma X. The clinical phenotypes of autoimmune hepatitis: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2016;66:98-107. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2015.10.006.
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 2015;63:971-1004. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.06.030.
Manns M, Lohse A, Vergani D. Autoimmune hepatitis-update 2015. J Hepatol. 2015;62:S100-11. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.03.005.
Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Autoimmune liver diseases in children-what is different from adulthood? Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;25:783-95. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2011.10.007.
Liberal R, Grant C, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Autoimmune hepatitis: a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2013;41:126-39. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2012.11.002.
Heneghan M, Yeoman A, Verma S, Smith A, Longhi MS. Autoimmune hepatitis. Lancet. 2013;382:1433-44. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62163-1.
Carbone M, Neuberger J. Autoimmune liver disease, autoimmunity and liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2014;60:210-23. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.09.020.
Pathak S, Kamat D. Autoimmune hepatitis in children. Pediatr Ann. 2018;47:e81-6. doi: https://doi.org/10.3928/19382359-20180126-01.
Boberg K. Prevalence and epidemiology of autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Liver Dis. 2002;6:635-47. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1089-3261(02)00021-1.
Vitfell-Pedersen J, Jørgensen M, Müller K, Heilmann C. Autoimmune hepatitis in children in Eastern Denmark. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;55:376-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182602b20.
Gatselis N, Zachou K, Koukoulis G, Dalekos G. Autoimmune hepatitis, one disease with many faces: etiopathogenetic, clinico-laboratory and histological characteristics. World J Gastroenterol. 2015;21:60-83. doi: https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i1.60.
Tucker S, Jonas M, Perez-Atayde A. Hyaline droplets in Kupffer cells: a novel diagnostic clue for autoimmune hepatitis. Am J Surg Pathol. 2015;39:772-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000395.
Sahebjam F, Vierling J. Autoimmune hepatitis. Front Med. 2015;9:187-219. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-015-0386-y.
Johnson P, McFarlane I. Meeting report: International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group. Hepatology. 1993;18:998-1005. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840180435.
Álvarez F, Berg P, Bianchi F, Bianchi L, Burroughs A, Cancado E, et al. International Autoimmune Hepatitis Group Report: review of criteria for diagnosis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Hepatol. 1999;31:929-38. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(99)80297-9.
Liberal R, Grant C, Longhi M, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D. Diagnostic criteria of autoimmune hepatitis. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13:435-40. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2013.11.009.
Gregorio G, Portmann B, Reid F, Donaldson P, Doherty D, McCartney M, et al. Autoimmune hepatitis in childhood: a 20-year experience. Hepatology. 1997;25:541-7. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.510250308.
Floreani A, Liberal R, Vergani D, Mieli-Vergani G. Autoimmune hepatitis: contrasts and comparisons in children and adults-a comprehensive review. J Autoimmun. 2013;46:7-16. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaut.2013.08.004.
Krawitt E. Autoimmune hepatitis. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:54-66. doi: https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra050408.
Wong R, Gish R, Frederick T, Bzowej N, Frenette C. The impact of race/ethnicity on the clinical epidemiology of autoimmune hepatitis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2012;46:155-61. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e318228b781.
Czaja A. Autoimmune hepatitis in special patient populations. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2011;25:689-700. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2011.09.011.
Gregorio G, McFarlane B, Bracken P, Vergani D, Mieli-Vergani G. Organ and non-organ specific autoantibody titres and IgG levels as markers of disease activity: a longitudinal study in childhood autoimmune liver disease. Autoimmunity. 2002;35:515-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/0891693021000056721.
de Boer Y, van Nieuwkerk C, Witte B, Mulder C, Bouma G, Bloemena E. Assessment of the histopathological key features in autoimmune hepatitis. Histopathology. 2015;66:351-62. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12558.
Balitzer D, Shafizadeh N, Peters M, Ferrell L, Alshak N, Kakar S. Autoimmune hepatitis: review of histologic features included in the simplified criteria proposed by the international autoimmune hepatitis group and proposal for new histologic criteria. Mod Pathol. 2017;30:773-83. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/modpathol.2016.267.
Mileti E, Rosenthal P, Peters M. Validation and modification of simplified diagnostic criteria for autoimmune hepatitis in children. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;10:417-21. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2011.11.030.
Miao Q, Bian Z, Tang R, Zhang H, Wang Q, Huang S, et al. Emperipolesis mediated by CD8 T cells is a characteristic histopathologic feature of autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2015;48:226-35. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-014-8432-0.
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















