Enfermedad celíaca refractaria tipo 1: reporte de dos casos con diferentes enfoques terapéuticos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1271Palavras-chave:
enfermedad celíaca, Tratamiento, Diagnóstico, dieta sin gluten, budesonida, azatioprinaResumo
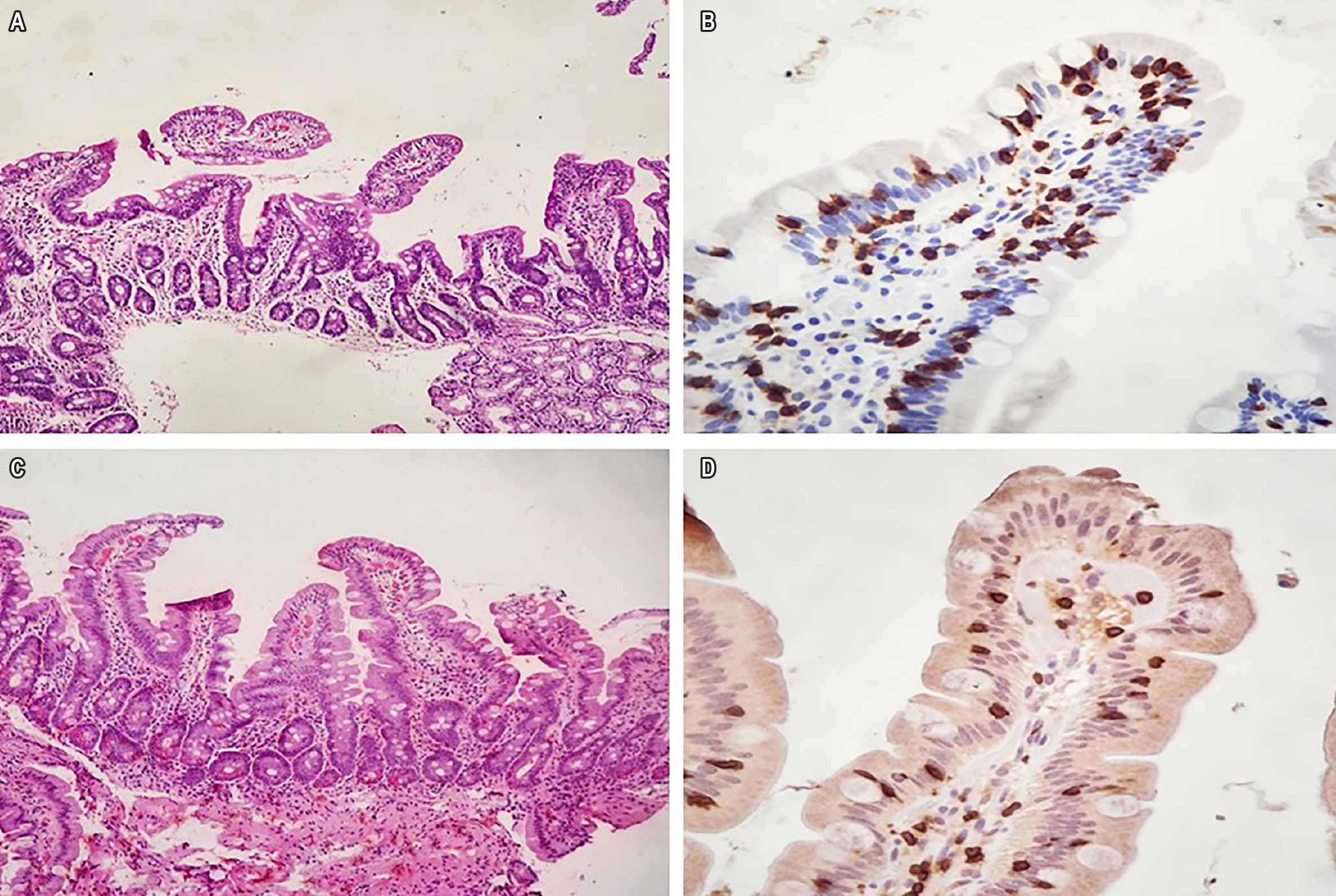
Antecedentes: la adherencia estricta durante toda la vida a una dieta libre de gluten (DLG) es el tratamiento eficaz para enfermedad celíaca (EC), que conduce a la remisión de síntomas y la curación de la mucosa. La enfermedad celíaca refractaria (ECR) se define como la persistencia o recaída de síntomas y daño intestinal en individuos previamente diagnosticados con EC después de al menos 12 meses de cumplimiento riguroso de DLG, que ocurre en una minoría de pacientes con EC. El diagnóstico y diferenciación del tipo de ECR se realiza mediante inmunohistoquímica específica en la biopsia duodenal.
Caso 1: Varón de 52 años con diagnóstico previo de EC que presentó síntomas incluso después de 5 años de un estricto cumplimiento de la DLG. El diagnóstico fue de ECR tipo 1 refractaria, tratado con budesonida oral (9 mg/día durante 8 meses), cuando se logró la remisión clínica, y la histopatología de la mucosa duodenal fue normal.
Caso 2: Mujer de 62 años con diagnóstico previo de EC y dos años de un estricto cumplimiento de la DLG, que presentó síntomas graves. El diagnóstico fue de ECR tipo 1, tratado con azatioprina en dosis de 2 mg/kg/día durante 24 meses, y se observó la remisión total de los síntomas y la recuperación de la mucosa duodenal.
Conclusiones: además del cumplimiento estricto de una dieta saludable sin gluten, tanto la budesonida oral como la azatioprina fueron eficaces en el tratamiento de ECR tipo 1, ya que los pacientes lograron y mantuvieron la remisión clínica sin los efectos secundarios de los fármacos.
Downloads
Referências
Al-Toma A, Volta U, Auricchio R, Castillejo G, Sanders DS, Cellier C, et al. European Society for the Study of Coeliac Disease (ESsCD) guideline for coeliac disease and other gluten-related disorders. United European Gastroenterol J. 2019;7(5):583-613. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640619844125
Green PHR, Paski S, Ko CW, Rubio-Tapia A. AGA Clinical Practice Update on Management of Refractory Celiac Disease: Expert Review. Gastroenterology. 2022;163(5):1461-1469. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.07.086
Rubio-Tapia A, Hill ID, Semrad C, Kelly CP, Greer KB, Limketkai BN, et al. American College of Gastroenterology Guidelines Update: Diagnosis and Management of Celiac Disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2023;118(1):59-76. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000002075
Tye-Din JA. Review article: Follow-up of coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;56 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S49-S63. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.16847
Silvester JA, Therrien A, Kelly CP. Celiac Disease: Fallacies and Facts. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(6):1148-1155. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001218
Volta U, Caio G, De Giorgio R. Mistakes in refractory coeliac disease and how to avoid them. UEG Education. 2019;19:15–18.
Penny HA, Baggus EMR, Rej A, Snowden JA, Sanders DS. Non-Responsive Coeliac Disease: A Comprehensive Review from the NHS England National Centre for Refractory Coeliac Disease. Nutrients. 2020;12(1):216. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010216
Rubio-Tapia A, Murray JA. Classification and management of refractory coeliac disease. Gut. 2010;59(4):547-57. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2009.195131
van Wanrooij RL, Müller DM, Neefjes-Borst EA, Meijer J, Koudstaal LG, Heideman DA, et al. Optimal strategies to identify aberrant intra-epithelial lymphocytes in refractory coeliac disease. J Clin Immunol. 2014;34(7):828-35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-014-0075-7
Goerres MS, Meijer JW, Wahab PJ, Kerckhaert JA, Groenen PJ, Van Krieken JH, et al. Azathioprine and prednisone combination therapy in refractory coeliac disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;18(5):487-94. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01687.x
Malamut G, Afchain P, Verkarre V, Lecomte T, Amiot A, Damotte D, et al. Presentation and long-term follow-up of refractory celiac disease: comparison of type I with type II. Gastroenterology. 2009;136(1):81-90. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.09.069
Soldera J, Salgado K, Pêgas KL. Refractory celiac disease type 2: how to diagnose and treat? Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2021;67(2):168-172. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9282.67.02.20200618
Rubio-Tapia A, Hill ID, Kelly CP, Calderwood AH, Murray JA; American College of Gastroenterology. ACG clinical guidelines: diagnosis and management of celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(5):656-76; quiz 677. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.79
Marsh MN. Mucosal pathology in gluten sensitivity. En: Marsh MN (editor). Coeliac disease. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1992. p. 136-991.
Oberhuber G, Granditsch G, Vogelsang H. The histopathology of coeliac disease: time for a standardized report scheme for pathologists. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1999;11(10):1185-94. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-199910000-00019
Patey-Mariaud De Serre N, Cellier C, Jabri B, Delabesse E, Verkarre V, Roche B, et al. Distinction between coeliac disease and refractory sprue: a simple immunohistochemical method. Histopathology. 2000;37(1):70-7. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2559.2000.00926.x
Aziz M, Haghbin H, Khan RS, Khan Z, Weissman S, Kamal F, et al. Celiac Disease Is Associated with Microscopic Colitis in Refractory Cases in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Dig Dis Sci. 2022;67(8):3529-3542. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-021-07232-7
Demiroren K. Possible relationship between refractory celiac disease and malignancies. World J Clin Oncol. 2022;13(3):200-208. https://doi.org/10.5306/wjco.v13.i3.200
Packova B, Kohout P, Dastych M, Prokesova J, Grolich T, Kroupa R. Malignant complications of celiac disease: a case series and review of the literature. J Med Case Rep. 2022;16(1):460. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-022-03682-3
Mukewar SS, Sharma A, Rubio-Tapia A, Wu TT, Jabri B, Murray JA. Open-Capsule Budesonide for Refractory Celiac Disease Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(6):959-967. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2017.71
Edsbäcker S, Bengtsson B, Larsson P, Lundin P, Nilsson A, Ulmius J, et al. A pharmacoscintigraphic evaluation of oral budesonide given as controlled-release (Entocort) capsules. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2003;17(4):525-36. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01426.x
Tack GJ, van Asseldonk DP, van Wanrooij RL, van Bodegraven AA, Mulder CJ. Tioguanine in the treatment of refractory coeliac disease--a single centre experience. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2012;36(3):274-81. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2012.05154.x
Iqbal U, Chaudhary A, Karim MA, Anwar H, Merrell N. Refractory celiac disease successfully treated with azathioprine. Gastroenterology Res. 2017;10(3):199-201. https://doi.org/10.14740/gr819w
Jiang C, Barkin JA, Barkin JS. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Is Common in Celiac Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2023;68(8):3421-3427. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-023-07965-7
Leonard MM, Cureton P, Fasano A. Indications and Use of the Gluten Contamination Elimination Diet for Patients with Non-Responsive Celiac Disease. Nutrients. 2017;9(10):1129. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu9101129
Raiteri A, Granito A, Giamperoli A, Catenaro T, Negrini G, Tovoli F. Current guidelines for the management of celiac disease: A systematic review with comparative analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2022;28(1):154-175. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v28.i1.154
Downloads
Publicado
Como Citar
Edição
Seção
Licença
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterologia

Este trabalho está licenciado sob uma licença Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.