Recurrence in patients with epiploic appendagitis: A case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.901Keywords:
Recurrence, Abdominal Pain, Case reportsAbstract
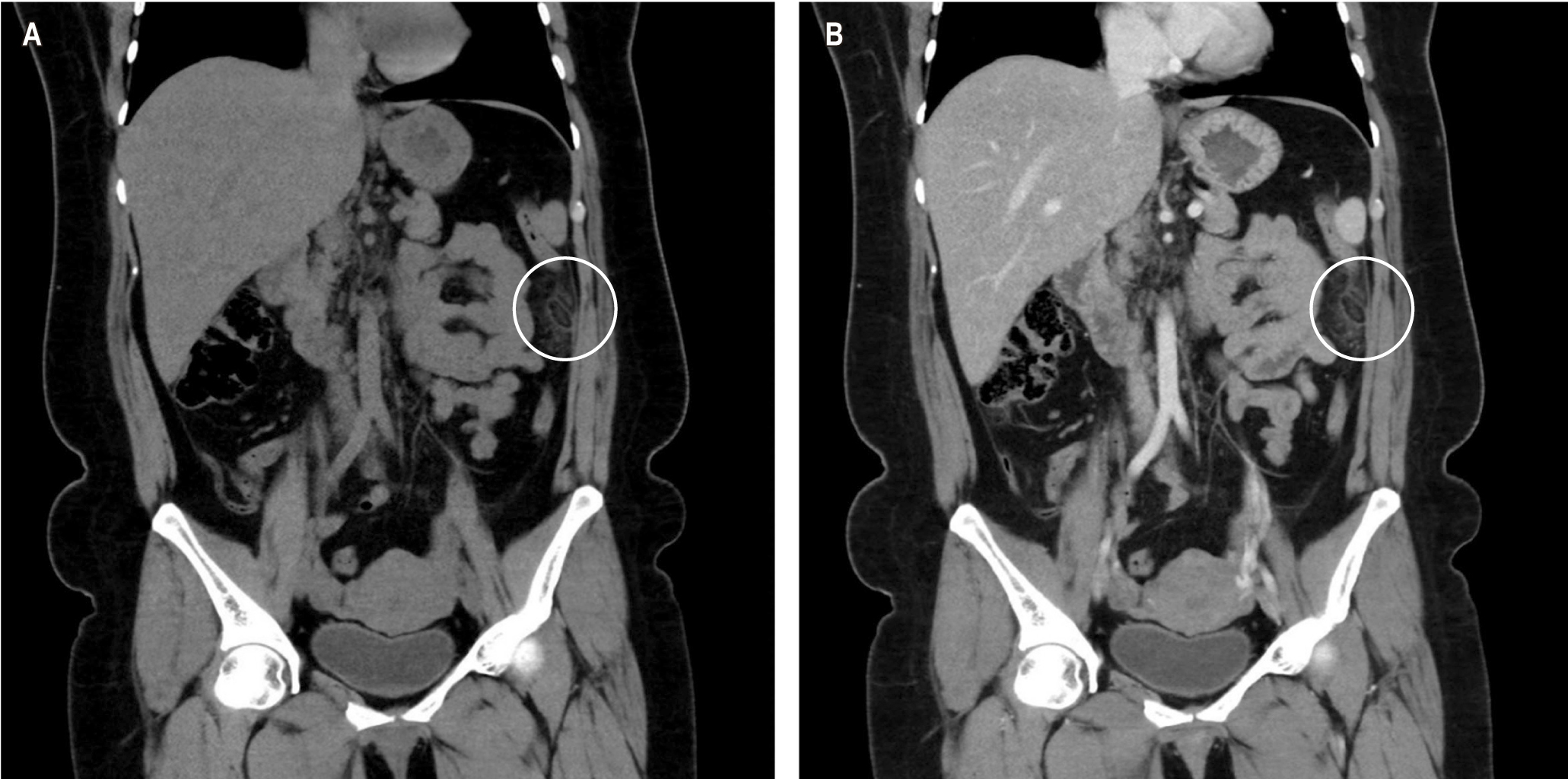
Epiploic appendagitis is a rare cause of acute abdominal pain. Management is self-limiting; however, some require surgical intervention. This case describes a 41-year-old female patient admitted to the emergency service for a clinical picture of an acute abdomen. On physical examination, the abdomen was soft, depressible, and painful on palpation in the left upper quadrant. A computerized axial tomography (CT) was requested, which revealed a hypodense oval image with a hyperdense center compatible with epiploic appendagitis. The patient received conservative therapy and was then discharged. Seven months later, the patient returned for an acute abdominal condition; complementary tests were negative, and she was treated again with conservative therapy. For 12 months, the patient has not relapsed. This case describes the recurrences in this rare pathology and the treatment that should be evaluated to avoid these relapses.
Downloads
References
Suresh Kumar VC, Mani KK, Alwakkaa H, Shina J. Epiploic Appendagitis: An Often Misdiagnosed Cause of Acute Abdomen. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019;13(3):364-8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502683
Sand M, Gelos M, Bechara FG, Sand D, Wiese TH, Steinstraesser L, et al. Epiploic appendagitis - Clinical characteristics of an uncommon surgical diagnosis. BMC Surgery. 2007;7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2482-7-11
Danielson K, Chernin MM, Amberg JR, Goff S, Durham JR. Epiploic Appendicitis: CT Characteristics. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1986;10(1):142-3. https://doi.org/10.1097/00004728-198601000-00032
Ozdemir S, Gulpinar K, Leventoglu S, Uslu HY, Turkoz E, Ozcay N, et al. Torsion of the primary epiploic appendagitis: a case series and review of the literature. Am J Surg. 2010;199(4):453-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2009.02.004
Dockerty L, Lynn T, Waugh J. A clinicopathologic study of the epiploic appendages. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1956;103(4):423-33.
Schnedl WJ, Krause R, Tafeit E, Tillich M, Lipp RW, Wallner-Liebmann SJ. Insights into epiploic appendagitis. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2011;8(1):45-9. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2010.189
de Brito P, Gomez MA, Besson M, Scotto B, Huten N, Alison D. Fréquence et épidémiologiedescriptive de l’appendicite épiploïque primitive par l’exploration tomodensitométrique des douleurs abdominales de l’adulte. J Radiol. 2008;89(2):235-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0221-0363(08)70399-8
Suresh Kumar VC, Mani KK, Alwakkaa H, Shina J. Epiploic Appendagitis: An Often Misdiagnosed Cause of Acute Abdomen. Case Rep Gastroenterol. 2019;13(3):364–8. https://doi.org/10.1159/000502683
Giannis D, Matenoglou E, Sidiropoulou MS, Papalampros A, Schmitz R, Felekouras E, et al. Epiploic appendagitis: pathogenesis, clinical findings and imaging clues of a misdiagnosed mimicker. Annals of Translational Medicine. 2019;7(24):814. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2019.12.74
Singh AK, Gervais DA, Hahn PF, Sagar P, Mueller PR, Novelline RA. Acute epiploic appendagitis and its mimics. Radiographics. 2005;25(6):1521-34. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.256055030
Choi YU, Choi PW, Park YH, Kim JI, Heo TG, Park JH, et al. Clinical Characteristics of Primary Epiploic Appendagitis. J Korean Soc Coloproctol. 2011;27(3):114-21. https://doi.org/10.3393/jksc.2011.27.3.114
Giambelluca D, Cannella R, Caruana G, Salvaggio L, Grassedonio E, Galia M, et al. CT imaging findings of epiploic appendagitis: an unusual cause of abdominal pain. Insights into Imaging. 2019;10(1):26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13244-019-0715-9
Lorente C, B. Hearne C, Taboada J. Recurrent epiploic appendagitis mimicking appendicitis and cholecystitis. Proc (Bayl Univ Med Cent). 2017;30(1):44–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/08998280.2017.11929522
Vázquez-Frias JA, Castañeda P, Valencia S, Cueto J. Laparoscopic Diagnosis and Treatment of an Acute Epiploic Appendagitis with Torsion and Necrosis Causing an Acute Abdomen. JSLS. 2000;4(3):247-50.
Donohue SJ, Reinke CE, Evans SL, Jordan MM, Warren YE, Hetherington T, et al. Laparoscopy is associated with decreased all-cause mortality in patients undergoing emergency general surgery procedures in a regional health system. Surg Endosc. 2021; 36(6):3822-3832. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08699-1
Choi YI, Woo HS, Chung JW, Shim YS, Kwon KA, Kim KO, et al. Primary epiploic appendagitis: Compared with diverticulitis and focused on obesity and recurrence. Intestinal Research. 2019;17(4):554–60.
Doğan AN, Çakıroğlu B, Akça AH, Aksoy SH, Akar T. Primary epiploic appendagitis: evaluation of computed tomography findings in the differential diagnosis of patients that presented with acute abdominal pain. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022;26(1):59-63. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202201_27748.
García Marín A, Nofuentes Riera C, Mella Laborde M, Pérez López M, Pérez Bru S, Rubio Cerdido JM. Apendagitis epiploica, causa poco frecuente de dolor abdominal. Cirugía y Cirujanos. 2014;82(4):389-94.
Hasbahceci M, Erol C, Seker M. Epiploic appendagitis: Is there need for surgery to confirm diagnosis in spite of clinical and radiological findings? World J Surg. 2012;36(2):441-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-011-1382-2
Legome EL, Belton AL, Murray RE, Rao PM, Novelline RA. Epiploic appendagitis: the emergency department presentation. J Emerg Med. 2002;22(1):9-13. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0736-4679(01)00430-9
Mantoğlu B, Altıntoprak F, Akın E, Fırat N, Gönüllü E, Dikicier E. Does primer appendagitis epiploica require surgical intervention? Ulusal Travma ve Acil Cerrahi Dergisi. 2020;26(6):883–6. https://doi.org/10.14744/tjtes.2020.09693
Vázquez GM, Manzotti ME, Alessandrini G, Lemos S, Perret C, Catalano HN. Apendagitis epiploica primaria. Clínica y evolución de 73 casos. Medicina (Buenos Aires). 2014;74:448-50.
Yang L, Jia M, Han P. Primary epiploic appendagitis as an unusual cause of acute abdominal pain in a middle-aged male: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(33):e16846. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000016846
Yousaf A, Ahmad S, Ghaffar F, Sajid S, Ikram S. Bilateral Epiploic Appendagitis: A Rather Benign but Diagnostically Challenging Cause of Acute Abdominal Pain. Cureus. 2020;12(4):e7897. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7897
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















