Ulcerative Colitis Induced by Secukinumab in the Treatment of Ankylosing Spondylitis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.884Keywords:
Secukinumab, Ulcerative colitis, ankylosis espondilytisAbstract
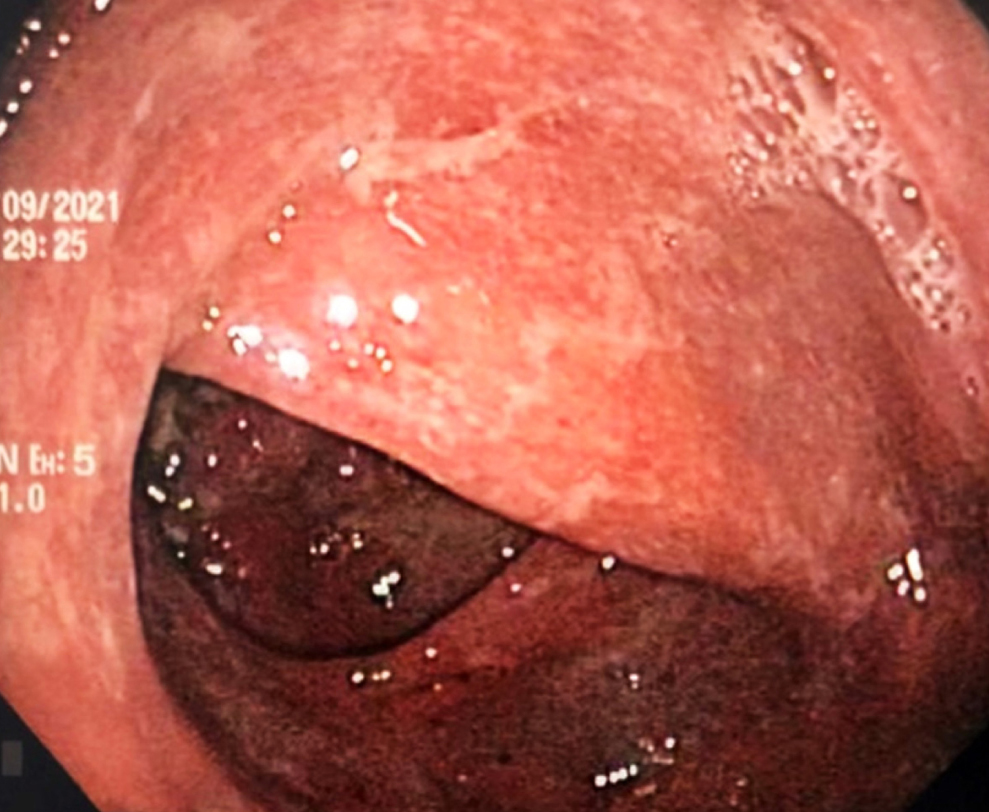
Interleukin 17 (IL-17) inhibitors are approved for treating psoriasis, psoriatic arthropathy, and ankylosing spondylitis. IL-17 is involved in the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); however, paradoxical events have been reported using selective IL-17 inhibitors such as secukinumab, whose pathophysiological mechanisms have not been fully clarified. Although the incidence of IBD in this group of patients is low, the risk could be reduced by carefully assessing risk factors such as family history, gastrointestinal symptoms, and fecal calprotectin before starting treatment.
Downloads
References
Kobayashi T, Okamoto S, Hisamatsu T, Kamada N, Chinen H, Saito R, et al. IL23 differentially regulates the Th1/Th17 balance in ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Gut. 2008;57(12):1682-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2007.135053
Abraham C, Dulai PS, Vermeire S, Sandborn WJ. Lessons Learned From Trials Targeting Cytokine Pathways in Patients With Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Gastroenterology. 2017;152(2):374-388.e4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.10.018
Wang J, Bhatia A, Cleveland NK, Gupta N, Dalal S, Rubin DT, et al. Rapid Onset of Inflammatory Bowel Disease after Receiving Secukinumab Infusion. ACG Case Reports J. 2018;5(1):e56. https://doi.org/10.14309/crj.2018.56
Whibley N, Gaffen SL. Gut-busters-IL-17 Ain't Afraid Of No IL-23 HHS Public Access. Immunity [Internet]. 2015;43(4):620-2. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4804829/pdf/nihms768634.pdf. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2015.10.001
Eichele DD, Kharbanda KK. Dextran sodium sulfate colitis murine model: An indispensable tool for advancing our understanding of inflammatory bowel diseases pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2017;23(33):6016-29. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i33.6016
Van Praet L, Van Den Bosch FE, Jacques P, Carron P, Jans L, Colman R, et al. Microscopic gut inflammation in axial spondyloarthritis: A multiparametric predictive model. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013;72(3):414-7. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202135
Onac IA, Clarke BD, Tacu C, Lloyd M, Hajela V, Batty T, et al. Secukinumab as a potential trigger of inflammatory bowel disease in ankylosing spondylitis or psoriatic arthritis patients. Rheumatology. 2021;1-6. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keab193
Emond B, Ellis LA, Chakravarty SD, Ladouceur M, Lefebvre P. Real-world incidence of inflammatory bowel disease among patients with other chronic inflammatory diseases treated with interleukin-17a or phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors. Curr Med Res Opin [Internet]. 2019;35(10):1751-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/03007995.2019.1620713
Caron B, Jouzeau JY, Miossec P, Petitpain N, Gillet P, Netter P, et al. Gastroenterological safety of IL-17 inhibitors: a systematic literature review. Expert Opin Drug Saf [Internet]. 2021;00(00):1-17. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1080/14740338.2021.1960981
Orrell KA, Murphrey M, Kelm RC, Lee HH, Pease DR, Laumann AE, et al. Inflammatory bowel disease events after exposure to interleukin 17 inhibitors secukinumab and ixekizumab: Postmarketing analysis from the RADAR ("Research on Adverse Drug events And Reports") program. J Am Acad Dermatol [Internet]. 2018;79(4):777-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2018.06.024
Schreiber S, Colombel JF, Feagan BG, Reich K, Deodhar AA, McInnes IB, et al. Incidence rates of inflammatory bowel disease in patients with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis treated with secukinumab: A retrospective analysis of pooled data from 21 clinical trials. Ann Rheum Dis. 2019;78(4):473-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-214273
Fauny M, Moulin D, D'Amico F, Netter P, Petitpain N, Arnone D, et al. Paradoxical gastrointestinal effects of interleukin-17 blockers. Ann Rheum Dis. 2020;79(9):1132-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217927
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


| Article metrics | |
|---|---|
| Abstract views | |
| Galley vies | |
| PDF Views | |
| HTML views | |
| Other views | |















