Intestinal mucosal lesion associated with crystals: Case series and literature review
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.834Keywords:
Bile acid sequestrants, Kayexalate, Crystal, Necrosis, Gastrointestinal tractAbstract
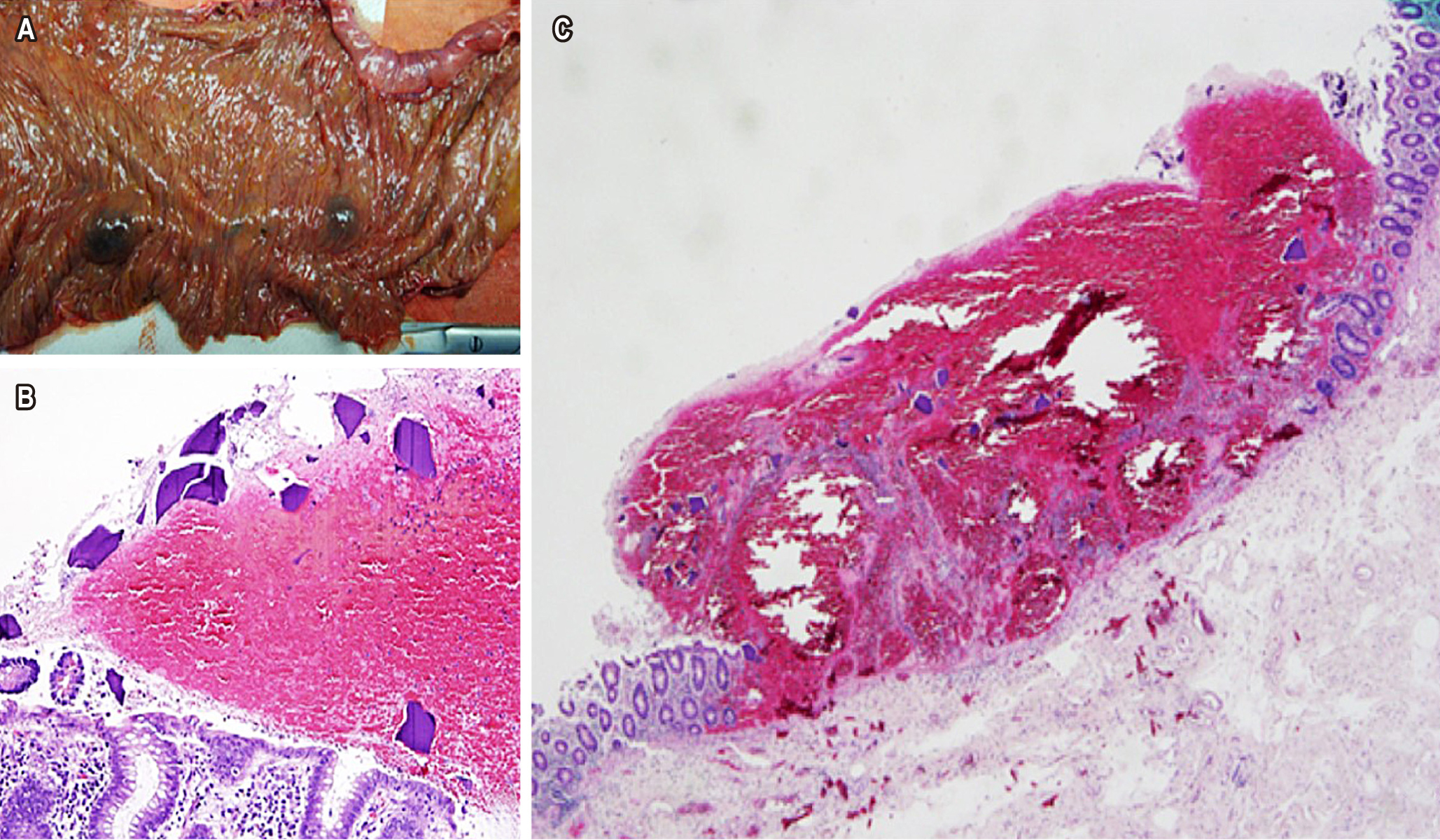
Crystal-associated mucosal injury is a crucial clinical picture in a subset of uremic patients who are given cation exchange resins such as sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) and sevelamer to treat hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia, respectively. Colonic necrosis in these patients is rare but may be associated with fatal gastrointestinal injury, with a mortality rate of 33%. Bile acid sequestrants are another type of resin that is theoretically biologically inert. Two cases of colitis associated with crystals are presented. The first patient had a history of multiple surgeries and pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract and was treated with cholestyramine. A sigmoidectomy was performed in which several crystal foci were found. The second patient had a history of chronic kidney disease requiring Kayexalate and attended the emergency department with severe lower GI bleeding. A partial colectomy was performed in which morphological changes related to the deposit of crystals were detected. Resins can cause a broad spectrum of malignant mucosal lesions, so early diagnosis is essential to reduce mortality and improve prognosis. However, it is uncertain whether the consumption of cholestyramine and kayexalate, as well as the deposition of their crystals in the GI tract, are the causative factor of mucosal damage. Therefore, resins should help establish the correct diagnosis and prompt medical treatment to avoid harmful results.
Downloads
References
Swanson BJ, Limketkai BN, Liu TC, Montgomery E, Nazari K, Park JY, et al. Sevelamer crystals in the gastrointestinal tract (GIT): A new entity associated with mucosal injury. Am J Surg Pathol. 2013;37(11):1686-93. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e3182999d8d
Harel Z, Harel S, Shah PS, Wald R, Perl J, Bell CM. Gastrointestinal adverse events with sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) use: A systematic review. Am J Med. 2013;126(3):264.e9-264.e24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2012.08.016
Arnold MA, Swanson BJ, Crowder CD, Frankel WL, Lam-Himlin D, Singhi AD, et al. Colesevelam and colestipol: Novel medication resins in the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38(11):1530-37. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0000000000000260
Gonzalez RS, Lagana SM, Szeto O, Arnold CA. Challenges in diagnosing medication resins in surgical pathology specimens: A crystal-clear review guide. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2017;141(9):1276-82. https://doi.org/10.5858/arpa.2016-0587-RA
Parfitt JR, Driman DK. Pathological effects of drugs on the gastrointestinal tract: a review. Hum Pathol. 2007;38(4):527-36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2007.01.014
Chatila AT, Bilal M, Merwat S. Kayexalate-Induced Colonic Pseudotumor. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;17(7):e73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2018.03.032
Huang D, Xiong M, Xu X, Wu X, Xu J, Cai X, et al. Bile acids elevated by high-fat feeding induce endoplasmic reticulum stress in intestinal stem cells and contribute to mucosal barrier damage. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;529(2):289-95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.226
Eastwood GL. Failure of cholestyramine to prevent bile salt injury to mouse gastric mucosa. Gastroenterology. 1975;68(6):1466-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5085(75)80133-8
Gonzalez RS, Schwartz DA, Shi C. Colestipol granules in the colon: Macroscopic and microscopic findings. Histopathology. 2015;67(1):141-42. https://doi.org/10.1111/his.12618
Abraham SC, Bhagavan BS, Lee LA, Rashid A, Wu TT. Upper Gastrointestinal Tract Injury in Patients Receiving Kayexalate (Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate) in Sorbitol: Clinical, Endoscopic, and Histopathologic Findings. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25(5): 637-44. https://doi.org/10.1097/00000478-200105000-00011
Okayama K, Hirata Y, Kumai D, Yamamoto Y, Kojima Y, Kanno T, et al. The Successful Treatment of Sodium Polystyrene Sulfonate-induces Enteritis Diagnosed by Small Bowel Endoscopy. Intern Med. 2018;57(11):1577-81. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.0088-17
Kumar K, Patel H, Saad M, Baiomi A, Dev A. Kayexalate-Induced Esophageal Ulceration in a Patient with Decompensated Cirrhosis: A Review of the Literature. Case Rep Gastrointest Med. 2021;2021:8831814. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/8831814
Georgianos PI, Liampas I, Kyriakou A, Vaios V, Raptis V, Savvidis N, et al. Evaluation of the tolerability and efficacy of sodium polystyrene sulfonate for long-term management of hyperkalaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol. 2017;49(12):2217-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-017-1717-5
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















