Strongyloides stercolaris hyperinfection in a young patient with HTLV-1 infection and ulcerative colitis
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.688Keywords:
Strongyloides, Human T-lymphotropic virus type 1, Pulmonary eosinophilia, Ulcerative colitisAbstract
Strongyloidiasis is an infection caused by the strongyloides stercolaris (SS) parasite, it is associated with high mortality in immunosuppressed patients due to larval dissemination and hyperinfection syndrome. Gastric mucosa involvement is rare, but when it occurs it is characterized by digestive bleeding and persistent emesis. We present the case of a 27 year old patient with gastrointestinal symptoms, a history of HTLV-1 infection and ulcerative colitis, who developed SS hyperinfection syndrome. The clinical presentation, diagnosis, treatment and complications derived from the infectious disease are described.
Downloads
References
Mathison BA, Pritt BS. 2019. Medical parasitology taxonomy update, 2016 –2017. J Clin Microbiol 57:e01067-18. https://doi.org/10.1128/JCM.01067-18.
Wang LF, Xu L, Luo SQ, Xie H, Chen W, Wu ZD, Sun X. Diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis by morphological characteristics combine with molecular biological methods. Parasitol Res. 2017;116(4):1159-63. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-017-5389-y
González-Horna PJ, Iglesias-Osores SA. Morfología de Strongyloides stercoralis. Rev del Cuerpo Médico del HNAAA. 2018;10(3):169-70. https://doi.org/10.35434/rcmhnaaa.2017.103.11
Grove DI. Leading article-Tropical infection of the gastrointestinal tract and liver series Strongyloidiasis: a conundrum for gastroenterologists. Gut. 1994;35(4):437-40. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.35.4.437
Schär F, Trostdorf U, Giardina F, Khieu V, Muth S, Marti H, Vounatsou P, Odermatt P. Strongyloides stercoralis: Global Distribution and Risk Factors. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7(7):1-17. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0002288
Greaves D, Coggle S, Pollard C, Aliyu SH, Moore EM. Strongyloides stercoralis infection. BMJ. 2013;347(7919):1-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f4610
Ghosh K, Ghosh K. Strongyloides stercoralis septicaemia following steroid therapy for eosinophilia: report of three cases. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 2007;101(11):1163-5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.05.021
Roxby. AC, Gottlieb. GS, Limaye AP. Strongyloidiasis in transplant patients. Clin Infect Dis. 2009;49(9):1411-23.
https://doi.org/10.1086/630201
Verdonck K, González E, Van Dooren S, Vandamme AM, Vanham G, Gotuzzo E. Human T-lymphotropic virus 1: recent knowledge about an ancient infection. Lancet Infect Dis. 2007;7(4):266-81. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70081-6
Terashima A, Alvarez H, Tello R, Infante R, Freedman DO, Gotuzzo E. Treatment failure in intestinal strongyloidiasis: An indicator of HTLV-I infection. Int J Infect Dis. 2002;6(1):28-30. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1201-9712(02)90132-3
Vadlamudi RS, Chi DS, Krishnaswamy G. Intestinal strongyloidiasis and hyperinfection syndrome. Clin Mol Allergy. 2006;4:1-13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-7961-4-8
Corti M. Strongyloides stercoralis in immunosuppressed patients. Arch Clin Infect Dis. 2016;11(1):1-10.
https://doi.org/10.5812/archcid.27510
Buonfrate D, Formenti F, Perandin F, Bisoffi Z. Novel approaches to the diagnosis of Strongyloides stercoralis infection. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2015;21(6):543-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2015.04.001
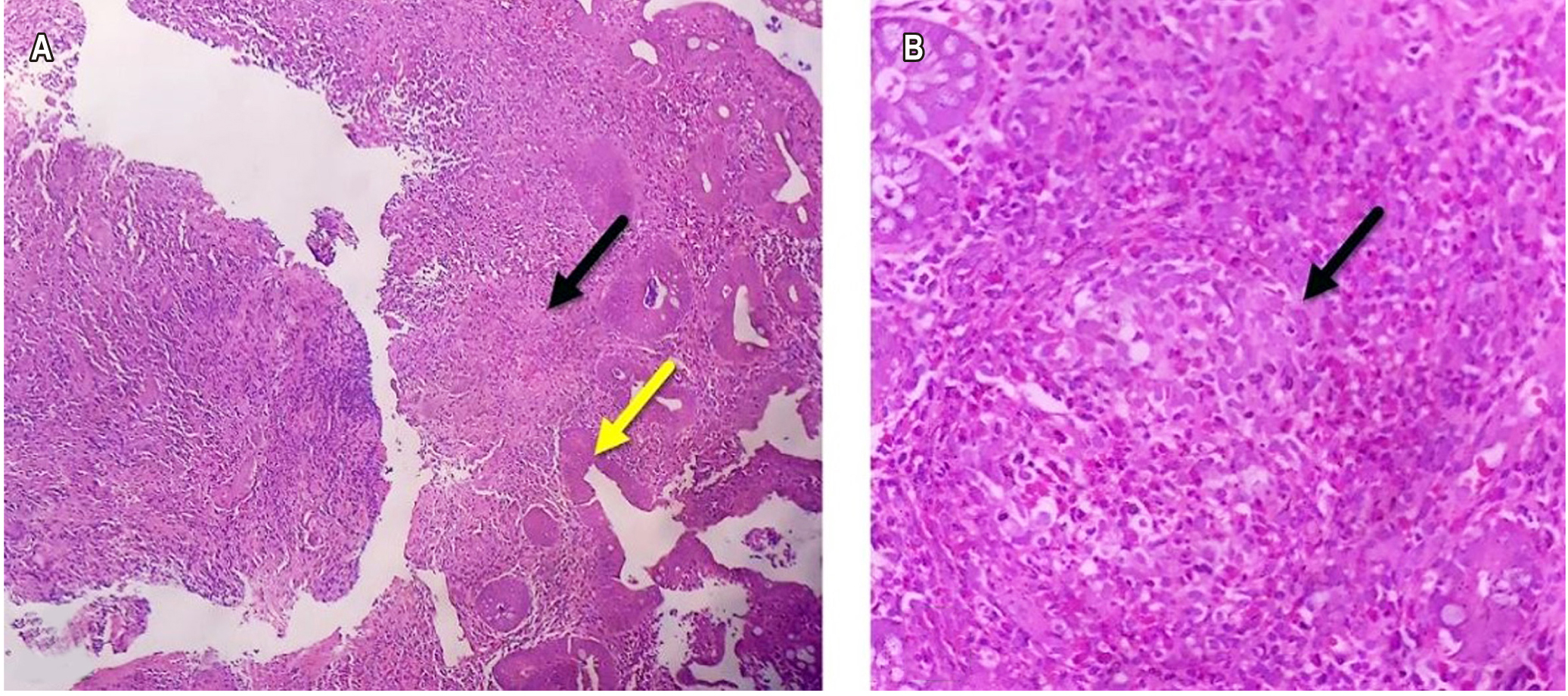
Qu Z, Kundu UR, Abadeer RA, Wanger A. Strongyloides colitis is a lethal mimic of ulcerative colitis: the key morphologic differential diagnosis. Hum Pathol. 2009;40(4):572-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humpath.2008.10.008
Poveda J, El-Sharkawy F, Arosemena LR, García-Buitrago MT, Rojas CP. Strongyloides Colitis as a Harmful Mimicker of Inflammatory Bowel Disease . Case Rep Pathol. 2017;2017:1-4. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/2560719
Suzuki Y, Suda T. Eosinophilic pneumonia: A review of the previous literature, causes, diagnosis, and management. Allergol Int. 2019;68(4):413-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2019.05.006
DiGiulio M. Strongyloidiasis. J Nurse Pract. 2019;15(6):438-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurpra.2019.03.015
Erstad BL. Albumin disposition in critically Ill patients. J Clin Pharm Ther. 2018;43(5):746-51. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.12742
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















