Proton Pump Inhibitors and Quality of Life in Patients with Globus Pharyngeus: An Observational Study
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1178Keywords:
globus pharingeo, Globus Pharyngeus, quality of life, Proton pump inhibitor, gastroesophageal refluxAbstract
Introduction: Globus pharyngeus accounts for up to 4% of otolaryngology consultations. There is no consensus in the literature regarding its treatment; however, most studies agree that gastroesophageal reflux is the primary etiological factor.
Objective: To determine whether treatment with proton pump inhibitors is associated with changes in the quality of life of patients with globus pharyngeus.
Methods: This prospective observational study included patients who attended otolaryngology outpatient consultations between January and December 2022 and were diagnosed with globus pharyngeus. All patients underwent a comprehensive otolaryngologic evaluation, and the following assessment tools were used before and after three months of treatment: the Reflux Symptom Index (RSI), the Reflux Finding Score (RFS), the Glasgow-Edinburgh Throat Scale (GETS) for globus pharyngeus, and the SF-36 Quality of Life Questionnaire.
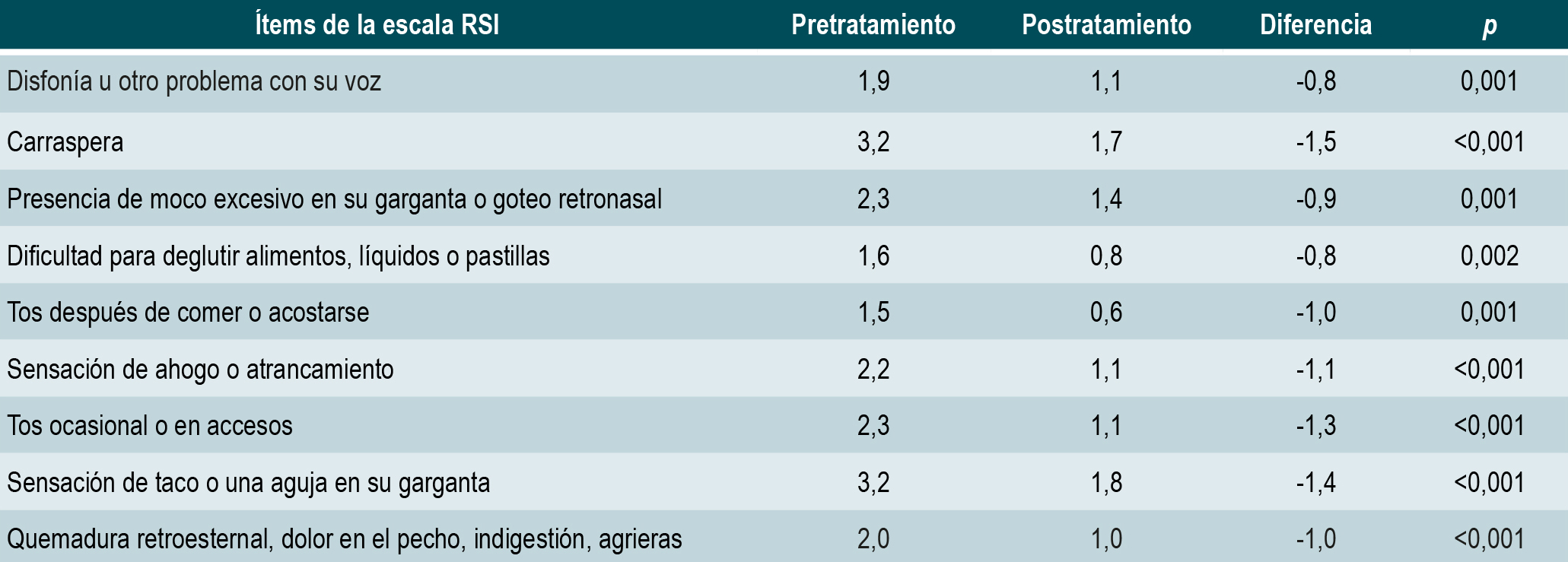
Results: The study population consisted of 35 patients, 27 of whom were women (77.1%), with an average age of 55.2 years. Improvement was observed in all RSI scale parameters. Quality of life improved after treatment in the domains of bodily pain, vitality, social functioning, emotional role, and mental health.
Conclusions: In this observational study, treatment with proton pump inhibitors significantly improved symptoms associated with globus pharyngeus.
Downloads
References
Delaine E, Asimakopoulos A, Avagnina A, Hallak B, Bouayed S. Dysphagia with no obvious cause: globus pharyngeus. Revue Medicale Suisse. 2022;18(803);2121-2125. https://doi.org/10.53738/REVMED.2022.18.803.2121
Drossman D, Li Z, Andruzzi E, Temple R, Talley N, Grant-Thompson W, et al. U. S. Householder survey of functional gastrointestinal disorders - Prevalence, sociodemography, and health impact. Dig Dis Sci. 1993;38(9):1569-80. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01303162
Harvey P, Theron B, Trudgill N. Managing a patient with globus pharyngeus. Frontline Gastroenterol. 2018;9(3):208-212. https://doi.org/10.1136/flgastro-2017-100844
Thompson W, Heaton K. Heartburn and globus in apparently healthy people. Can Med Assoc J. 1982;126(1):46-8.
Fukuhara T, Matsuda E, Ogawa A, Donishi R, Koyama S, Fujiwara K. Use of cervical ultrasonography in globus sensation investigation: a retrospective cohort study. Yonago Acta Medica. 2021;64(4):360-363. https://doi.org/10.33160/yam.2021.11.007
Deary IJ, Wilson JA, Kelly SW. Globus pharyngis, personality, and psychological distress in the general population. Psychosomatics. 1995;36(6):570-577. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0033-3182(95)71614-0
Penović S, Roje Ž, Brdar D, Gračan S, Bubić A, Vela J, et al. Globus Pharyngeus: A Symptom of Increased Thyroid or Laryngopharyngeal Reflux? Acta Clin Croat. 2018;57(1):110-115. https://doi.org/10.20471/acc.2018.57.01.13
Webb CJ, Makura ZG, Fenton JE, Jackson SR, McCormick MS, Jones AS. Globus pharyngeus: a postal questionnaire survey of UK ENT consultants. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 2000;25(6):566-9. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2273.2000.00386.x
McCall WV, Athanasiadi A, Bowie C, Rosenquist PB. Major Depressive Disorder in the Older Adult Associated With Globus Pharyngeus and Weight Loss - An Indication for Electroconvulsive Therapy. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2022;30(2):235-239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jagp.2021.10.010
Khan MR, Saha M, Mamun MA, Salam KS, Chowdhury MS, Haque MM, et al. Upper GIT Endoscopic Evaluation and Psychological State Assessment of Patients with Globus Sensation. Mymensingh Med J. 2019;28(2):405-409.
Järvenpää P, Laatikainen A, Roine R, Sintonen H, Arkkila P, Aaltonen L. Symptom relief and health-related quality of life in globus patients: a prospective study. Logop Phoniatr Vocology. 2019;44(2):67-72. https://doi.org/10.1080/14015439.2017.1397741
Hamilton NJI, Wilcock J, Hannan SA. A lump in the throat: laryngopharyngeal reflux. BMJ. 2020;371:m4091. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.m4091
Kavookjian H, Irwin T, Garnett JD, Kraft S. The Reflux Symptom Index and Symptom Overlap in Dysphonic Patients. Laryngoscope. 2020;130(11):2631-2636. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.28506
Takahashi N, Mori K, Baba H, Sasaki T, Ohno M, Ikarashi F, et al. Reliability and validity of the Japanese version of the Glasgow Edinburgh Throat Scale (GETS-J): Use for a symptom scale of globus sensation. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2018;45(5):1041-1046. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2018.02.001
Boom L, Edens M, Rinia B. Reflux finding score and reflux symptom index as potential predictors for proton pump inhibitor response in globus pharyngeus patients: A prospective study. Auris Nasus Larynx. 2020;47(4):609-615. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2020.02.002
Von E, Altman D, Egger M, Pocock S, Gøtzsche P, Vandenbroucke J. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2008;61(4):344-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2007.11.008
Siupsinskiene N, Adamonis K, Toohill R, Sereika R. Predictors of response to short-term proton pump inhibitor treatment in laryngopharyngeal reflux patients. J Laryngol Otol. 2008;122(11):1206-12. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022215108001898
Rasmussen ER, Schnack DT, Ravn AT. A prospective cohort study of 122 adult patients presenting to an otolaryngologist’s office with globus pharyngeus. Clin Otolaryngol. 2018;43(3):854-860. https://doi.org/10.1111/coa.13065
Bouchoucha M, Girault-Lidvan N, Hejnar M, Mary F, Airinei G, Benamouzig R. Clinical and psychological characteristics of patients with globus. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 2019;43(5):614-622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinre.2019.01.006
Harris M, Deary I, Wilson J. Life events and difficulties in relation to the onset of globus pharyngis. J Psychosom Res. 1996;40(6):603-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-3999(96)00024-4
Fuchs HF, Müller DT, Berlth F, Maus MK, Fuchs C, Dübbers M, et al. Simultaneous laryngopharyngeal pH monitoring (Restech) and conventional esophageal pH monitoring-correlation using a large patient cohort of more than 100 patients with suspected gastroesophageal reflux disease. Dis Esophagus. 2018;31(10). https://doi.org/10.1093/dote/doy018
Chen J, Brady P. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterology Nursing. 2019;42(1):20-28. https://doi.org/10.1097/SGA.0000000000000359
Massawe WA, Nkya A, Abraham ZS, Babu KM, Moshi N, Kahinga AA, et al. Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease, prevalence and clinical characteristics in ENT department of a tertiary hospital Tanzania. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;7(1):28-33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wjorl.2020.04.009
Poovipirom N, Ratta‐apha W, Maneerattanaporn M, Geeratragool T, Chuenprapai P, Leelakusolvong S. Treatment outcomes in patients with globus: A randomized control trial of psychoeducation, neuromodulators, and proton pump inhibitors. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2023;35(3):e14500. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14500
Aanen MC, Weusten BL, Numans ME, de Wit NJ, Samsom M, Smout AJ. Effect of proton-pump inhibitor treatment on symptoms and quality of life in GERD patients depends on the symptom-reflux association. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2008;42(5):441-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e318074dd62
Powell J, Cocks HC. Mucosal changes in laryngopharyngeal reflux--prevalence, sensitivity, specificity and assessment. Laryngoscope. 2013;123(4):985-91. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.23693
Horvath L, Hagmann P, Burri E, Kraft M. Evaluation of Oropharyngeal pH-Monitoring in the Assessment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux. J Clin Med. 2021;10(11):2409. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10112409
Shilpa C, Sandeep S, Chandresh S, Grampurohit A, Shetty TS. Laryngopharyngeal Reflux and GERD: Correlation Between Reflux Symptom Index and Reflux Finding Score. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2019;71(Suppl 1):684-688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-018-1480-7
Shires CB, Dewan K. Is there Really a Lump in My Throat? The Incidence and Implication of Vocal fold Abnormalities in Patients Presenting with Globus. J Voice. 2024;38(6):1419-1423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvoice.2022.05.008
Hamdan AL, Khalifee E, Ghanem A, Mansour H, Yammine E. Predictive value of globus pharyngeus in patients with functional dysphonia versus organic dysphonia. Laryngoscope. 2019;129(4):930-934. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.27493
Zerbib F, Rommel N, Pandolfino J, Gyawali CP. ESNM/ANMS Review. Diagnosis and management of globus sensation: A clinical challenge. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2020;32(9):e13850. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13850
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















