Automatic Auditing System for Endoscopic Exploration of the Stomach with Artificial Intelligence-Gastro UNAL: Gastroendoscopy UNit for Automatic Labeling
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1163Keywords:
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, artificial intelligence, diagnostic blind spots, neural networkAbstract
Introduction: Upper endoscopy is the standard method for diagnosing early-stage gastric cancer. However, according to estimates, up to 20% of tumors are not detected, and their accuracy may be affected by the variability in their performance. In Colombia, most diagnoses take place in advanced stages, which aggravates the problem. Protocols have been proposed to ensure the complete observation of areas prone to premalignant lesions to address variability.
Objective: To build and validate an automatic audit system for endoscopies using artificial intelligence techniques.
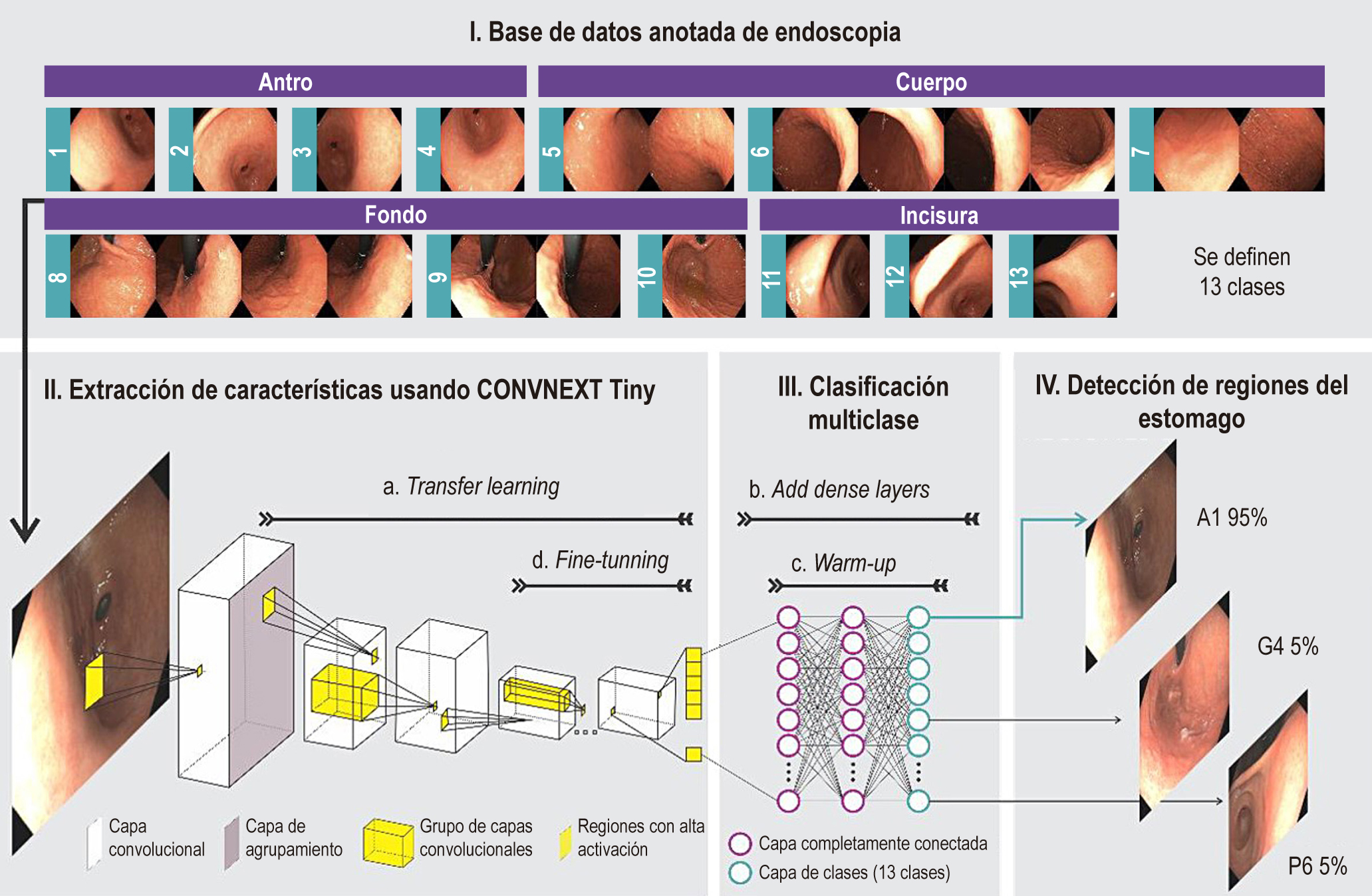
Methodology: In this study, 96 patients from a teaching hospital underwent video-documented endoscopies, spanning 22 stations rearranged to minimize overlaps and improve the identification of 13 key gastric regions. An advanced convolutional network was used to process the images, extracting visual characteristics, which facilitated the training of artificial intelligence in the classification of these areas.
Results: the model, called Gastro UNAL, was trained and validated with images of 67 patients (70% of cases) and tested with 29 different patients (30% of cases), which reached an average sensitivity of 85,5% and a specificity of 98,8% in detecting the 13 gastric regions.
Conclusions: The effectiveness of the model suggests its potential to ensure the quality and accuracy of endoscopies. This approach could confirm the regions evaluated, alerting less experienced or trained endoscopists about blind spots in the examinations, thus, increasing the quality of these procedures.
Downloads
References
Ferlay J, Ervik M, Lam F, Laversanne M, Colombet M, Mery L, et al. Global Cancer Observatory: Cancer Today [Internet]. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2024 [consultado el 1 de abril de 2024]. Disponible en: https://gco.iarc.who.int/today, accessed [01 04 2024].
Oliveros-Wilches R, Grillo-Ardila CF, Vallejo-Ortega M, Gil-Parada F, Cardona-Tobón M, Páramo-Hernández D, et al. Guía de práctica clínica para la prevención primaria y secundaria y diagnóstico temprano de cáncer gástrico. Rev Colomb Cancerol. 2022;26(1):39-96. https://doi.org/10.35509/01239015.754
Oliveros R, Navarrera LF. Diagnóstico, estadificación y tratamiento del cáncer gástrico en Colombia desde 2004 a 2008 (REGATE -Colombia). Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2012;27(4):269-74.
Pasechnikov V, Chukov S, Fedorov E, Kikuste I, Leja M. Gastric cancer: Prevention, screening and early diagnosis. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2014;20(38):13842-62. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i38.13842
Kaise M. Advanced endoscopic imaging for early gastric cancer. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2015;29(4):575-87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2015.05.010
Pimenta-Melo AR, Monteiro-Soares M, Libânio D, Dinis-Ribeiro M. Missing rate for gastric cancer during upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;28(9):1041-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000000657
Lee SH, Park YK, Cho SM, Kang JK, Lee DJ. Technical skills and training of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy for new beginners. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2015;21(3):759-85. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i3.759
Yao K. The endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer. Ann Gastroenterol Q Publ Hell Soc Gastroenterol. 2013;26(1):11.
Yao K, Uedo N, Muto M, Ishikawa H. Development of an e-learning system for teaching endoscopists how to diagnose early gastric cancer: basic principles for improving early detection. Gastric Cancer. 2017;20(Suppl 1):28-38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10120-016-0680-7
Kim JS, Kim BW. Training in Endoscopy: Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Clin Endosc. 2017;50(4):318-21. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2017.096
Eisen GM, Baron TH, Dominitz JA, Faigel DO, Goldstein JL, Johanson JF, et al. Methods of granting hospital privileges to perform gastrointestinal endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;55(7):780-3. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0016-5107(02)70403-3
Farthing MJ, Walt RP, Allan RN, Swan CH, Gilmore IT, Mallinson CN, et al. A national training programme for gastroenterology and hepatology. Gut. 1996;38(3):459-70. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.38.3.459
Beattie AD, Greff M, Lamy V, Mallinson CN. The European Diploma of Gastroenterology: progress towards harmonization of standards. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 1996;8(4):403-6. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-199604000-00021
Beg S, Ragunath K, Wyman A, Banks M, Trudgill N, Pritchard DM, et al. Quality standards in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: a position statement of the British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and Association of Upper Gastrointestinal Surgeons of Great Britain and Ireland (AUGIS). Gut. 2017;66(11):1886-99. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-314109
Bisschops R, Areia M, Coron E, Dobru D, Kaskas B, Kuvaev R, et al. Performance measures for upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: A European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy quality improvement initiative. United Eur Gastroenterol J. 2016;4(5):629-56. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640616664843
Yao K, Uedo N, Kamada T, Hirasawa T, Nagahama T, Yoshinaga S, et al. Guidelines for endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer. Dig Endosc Off J Jpn Gastroenterol Endosc Soc. 2020;32(5):663-98. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.13684
Emura F, Sharma P, Arantes V, Cerisoli C, Parra-Blanco A, Sumiyama K, et al. Principles and practice to facilitate complete photodocumentation of the upper gastrointestinal tract: World Endoscopy Organization position statement. Dig Endosc. 2020;32(2):168-79. https://doi.org/10.1111/den.13530
Kim GH, Bang SJ, Ende AR, Hwang JH. Is screening and surveillance for early detection of gastric cancer needed in Korean Americans? Korean J Intern Med. 2015;30(6):747-58. https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2015.30.6.747
Asaka M, Mabe K. Strategies for eliminating death from gastric cancer in Japan. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2014;90(7):251-8. https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.90.251
Hamashima C, Systematic Review Group and Guideline Development Group for Gastric Cancer Screening Guidelines. Update version of the Japanese Guidelines for Gastric Cancer Screening. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2018;48(7):673-83. https://doi.org/10.1093/jjco/hyy077
Yashima K, Shabana M, Kurumi H, Kawaguchi K, Isomoto H. Gastric Cancer Screening in Japan: A Narrative Review. J Clin Med. 2022;11(15):4337. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11154337
Goss PE, Lee BL, Badovinac-Crnjevic T, Strasser-Weippl K, Chavarri-Guerra Y, St Louis J, et al. Planning cancer control in Latin America and the Caribbean. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14(5):391-436. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70048-2
Bravo LE, Hernández Vargas JA, Collazos P, García LS, Valbuena AM, Acuña L. Survival in stomach cancer: analysis of a national cancer information system and a population-based cancer registry in Colombia. Colomb Médica CM. 2023;53(4):e2025126. https://doi.org/10.25100/cm.v53i4.5126
Liu Z, Mao H, Wu CY, Feichtenhofer C, Darrell T, Xie S. A ConvNet for the 2020s [Internet]. arXiv; 2022 [consultado el 15 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: http://arxiv.org/abs/2201.03545. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR52688.2022.01167
Bravo D, Ruano J, Jaramillo M, Gallego D, Gómez M, González FA, et al. Automatic Classification of Esophagogastroduodenoscopy Sub-Anatomical Regions. En: 2023 IEEE 20th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI). 2023. p. 1-5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ISBI53787.2023.10230483
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li LJ, Li K, Fei-Fei L. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. En: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2009. p. 248-55. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. ImageNet Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge [Internet]. arXiv; 2015 [consultado el 15 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0575
Serre T, Kreiman G, Kouh M, Cadieu C, Knoblich U, Poggio T. A quantitative theory of immediate visual recognition. Prog Brain Res. 2007;165:33-56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0079-6123(06)65004-8
Lee H, Ekanadham C, Ng A. Sparse deep belief net model for visual area V2 [Internet]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems; 2007 [consultado el 24 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: https://papers.nips.cc/paper_files/paper/2007/file/4daa3db355ef2b0e64b472968cb70f0d-Paper.pdf
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Deep Sparse Rectifier Neural Networks. International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics; 2011 [consultado el 24 de septiembre de 2023]. Disponible en: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Deep-Sparse-Rectifier-Neural-Networks-Glorot-Bordes/67107f78a84bdb2411053cb54e94fa226eea6d8e
Hamashima C, Ogoshi K, Narisawa R, Kishi T, Kato T, Fujita K, et al. Impact of endoscopic screening on mortality reduction from gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2015;21(8):2460-6. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i8.2460
Kim SY, Park JM. Quality indicators in esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Clin Endosc. 2022;55(3):319-31. https://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2022.094
Chiu PWY, Uedo N, Singh R, Gotoda T, Ng EKW, Yao K, et al. An Asian consensus on standards of diagnostic upper endoscopy for neoplasia. Gut. 2019;68(2):186-97. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2018-31711134.
Renna F, Martins M, Neto A, Cunha A, Libânio D, Dinis-Ribeiro M, et al. Artificial Intelligence for Upper Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Roadmap from Technology Development to Clinical Practice. Diagn Basel Switz. 2022;12(5):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12051278
Takiyama H, Ozawa T, Ishihara S, Fujishiro M, Shichijo S, Nomura S, et al. Automatic anatomical classification of esophagogastroduodenoscopy images using deep convolutional neural networks. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):7497. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25842-6
Wu L, Zhou W, Wan X, Zhang J, Shen L, Hu S, et al. A deep neural network improves endoscopic detection of early gastric cancer without blind spots. Endoscopy. 2019;51(6):522-31. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0855-3532
Chang YY, Li PC, Chang RF, Yao CD, Chen YY, Chang WY, et al. Deep learning-based endoscopic anatomy classification: an accelerated approach for data preparation and model validation. Surg Endosc. 2022;36(6):3811-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-021-08698-2
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















