Wilson’s Disease with Severe Neurological Presentation: A Case Report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1138Keywords:
Wilson disease, Dystonia, Penicillamine, CopperAbstract
Introduction: Wilson’s disease (WD) is an autosomal recessive disorder that can affect individuals of any age. Neurological involvement is reported in 30%–40% of patients, with dysarthria, ataxia, and dystonia being the primary manifestations. The presence of Kayser-Fleischer (KF) rings is observed in 77.2%–85.2% of cases. Chelation therapy demonstrates a paradoxical response in up to 50% of patients. We report a case of severe neurological presentation without KF rings, exhibiting a paradoxical response to chelation therapy.
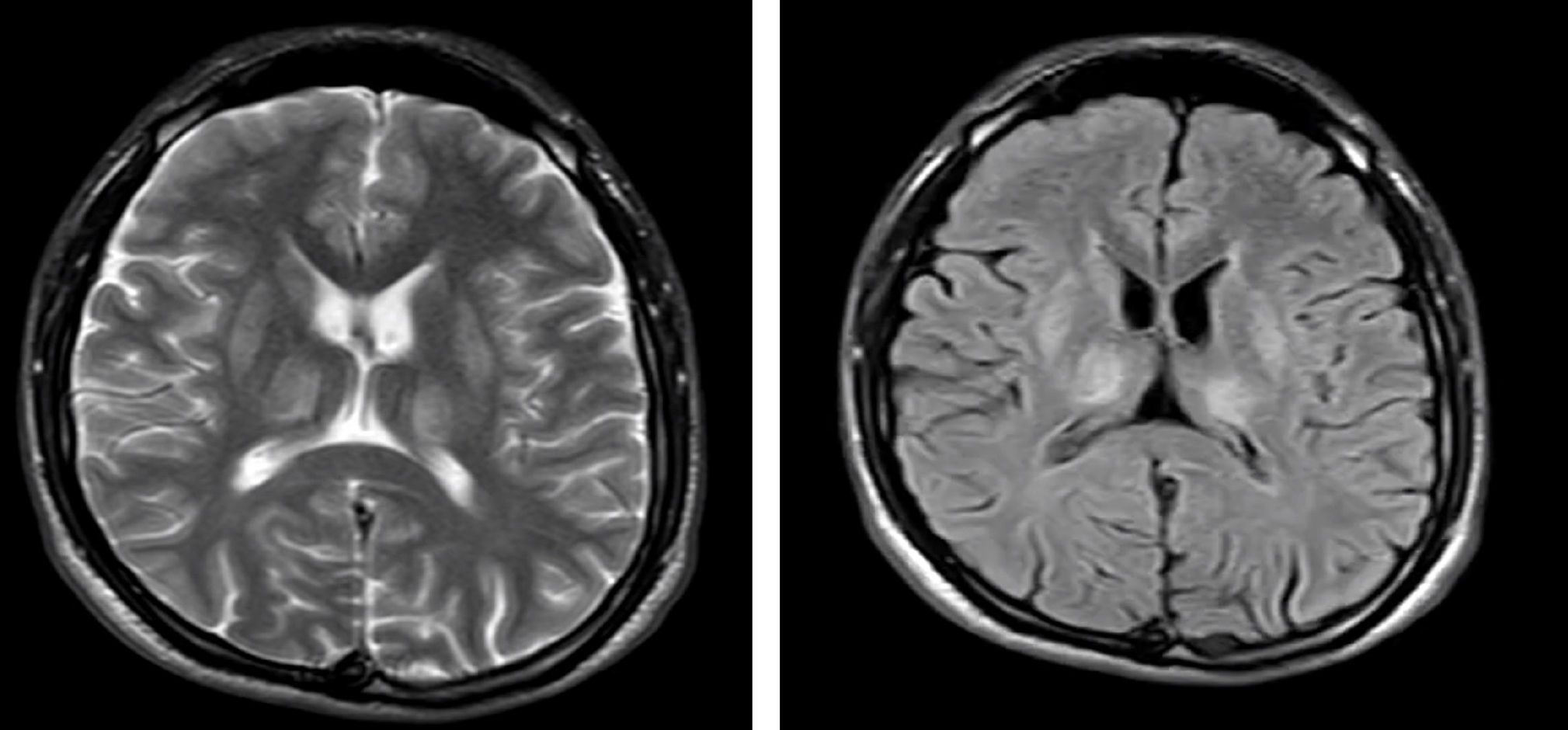
Case Presentation: A 23-year-old man with no prior medical history presented with a six-month history of symptoms consistent with vasovagal syncope episodes, followed by ataxia, muscle weakness, dysphagia, sialorrhea, and dysarthria. His condition progressively worsened due to sepsis of pulmonary origin secondary to an aspiration event. Investigations revealed low ceruloplasmin levels, elevated urinary copper, imaging findings consistent with thalamic and lenticular involvement, liver biopsy showing autoimmune hepatitis-like changes and features resembling non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), absence of KF rings, and a paradoxical response to chelation therapy. The disease course was marked by severe dystonia progression and a fatal outcome.
Conclusions: WD is a condition with significant morbidity and a variable clinical spectrum. Isolated neurological involvement without KF rings is uncommon, and outcomes depend on early initiation of copper chelation therapy. However, paradoxical worsening of symptoms due to treatment, as observed in this case, poses an additional challenge.
Downloads
References
Sharma N, Das DD, Chawla PA. Exploring the potential of trientine tetrahydrochloride in the treatment of Wilson disease. Heal Sci Rev. 2023;6:100082. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hsr.2023.100082
Vierling JM, Sussman NL. Wilson disease in adults: Clinical presentations, diagnosis, and medical management. En: Kerkar N, Roberts EA (editores). Clinical and Translational Perspectives on Wilson Disease. Elsevier; 2018. p. 165-177. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-810532-0.00016-1
Schilsky ML, Roberts EA, Bronstein JM, Dhawan A, Hamilton JP, Rivard AM, et al. A Multidisciplinary Approach to the Diagnosis and Management of Wilson Disease: 2022 Practice Guidance on Wilson Disease from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2022:1-49. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.32801
Muñoz Maya OG, Vélez Hernández JE, Santos Sánchez OM, Marín Zuluaga JI, Restrepo Gutiérrez JC. Enfermedad de Wilson: experiencia de un centro de referencia en Colombia. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2021;36(1):51-7. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.593
Sinha S, Taly AB, Ravishankar S, Prashanth LK, Venugopal KS, Arunodaya GR, et al. Wilson’s disease: cranial MRI observations and clinical correlation. Neuroradiology. 2006;48(9):613-21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0101-4
Ferrarese A, Morelli MC, Carrai P, Milana M, Angelico M, Perricone G, et al. Outcomes of Liver Transplant for Adults With Wilson’s Disease. Liver Transplant. 2020;26(4):507-16. https://doi.org/10.1002/lt.25714
European Association for Study of Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Wilson’s disease. J Hepatol. 2012;56(3):671-85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2011.11.007
Moini M, To U, Schilsky ML. Recent advances in Wilson disease. Transl Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;6:21. https://doi.org/10.21037/tgh-2020-02
Chevalier K, Mauget-Faÿsse M, Vasseur V, Azar G, Obadia MA, Poujois A. Eye Involvement in Wilson’s Disease: A Review of the Literature. J Clin Med. 2022;11(9):2528. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11092528
Członkowska A, Litwin T, Dusek P, Ferenci P, Lutsenko S, Medici V, et al. Wilson disease. Nat Rev Dis Prim. 2018;4(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-018-0018-3
Cope-Yokoyama S, Finegold MJ, Sturniolo GC, Kim K, Mescoli C, Rugge M, et al. Wilson disease: histopathological correlations with treatment on follow-up liver biopsies. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16(12):1487-94. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i12.1487
Gerosa C, Fanni D, Congiu T, Piras M, Cau F, Moi M, et al. Liver pathology in Wilson’s disease: From copper overload to cirrhosis. J Inorg Biochem. 2019;193:106-11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2019.01.008
Merle U, Schaefer M, Ferenci P, Stremmel W. Clinical presentation, diagnosis and long-term outcome of Wilson’s disease: a cohort study. Gut. 2007;56(1):115-20. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.087262
Schilsky ML, Czlonkowska A, Zuin M, Cassiman D, Twardowschy C, Poujois A, et al. Trientine tetrahydrochloride versus penicillamine for maintenance therapy in Wilson disease (CHELATE): a randomised, open-label, non-inferiority, phase 3 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;7(12):1092-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00270-9
Kim P, Zhang CC, Thoröe-Boveleth S, Buhl EM, Weiskirchen S, Stremmel W, et al. Analyzing the Therapeutic Efficacy of Bis-Choline-Tetrathiomolybdate in the Atp7b(-/-) Copper Overload Mouse Model. Biomedicines. 2021;9(12):1861. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9121861
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















