Reporte de caso de colestasis intrahepática asociada a mutación del gen ATP8B1 en un paciente con infección por virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH): un reto diagnóstico
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1120Palabras clave:
ictericia, colestasis intrahepática, mutaciónResumen
La colestasis intrahepática benigna recurrente (CIBR) es una entidad poco frecuente que hace parte de un espectro de trastornos conocidos como colestasis intrahepática familiar; se caracteriza por episodios de colestasis que duran de semanas a meses y tienen una resolución completa entre los mismos. Está asociada con buen pronóstico, a diferencia de otros, debido a su aparición en edades más tardías y a su menor asociación con fibrosis. El diagnóstico es de exclusión, implica un reto diagnóstico y, por tanto, un bajo umbral de sospecha, y se confirma con la mutación en el gen ATP8B1.
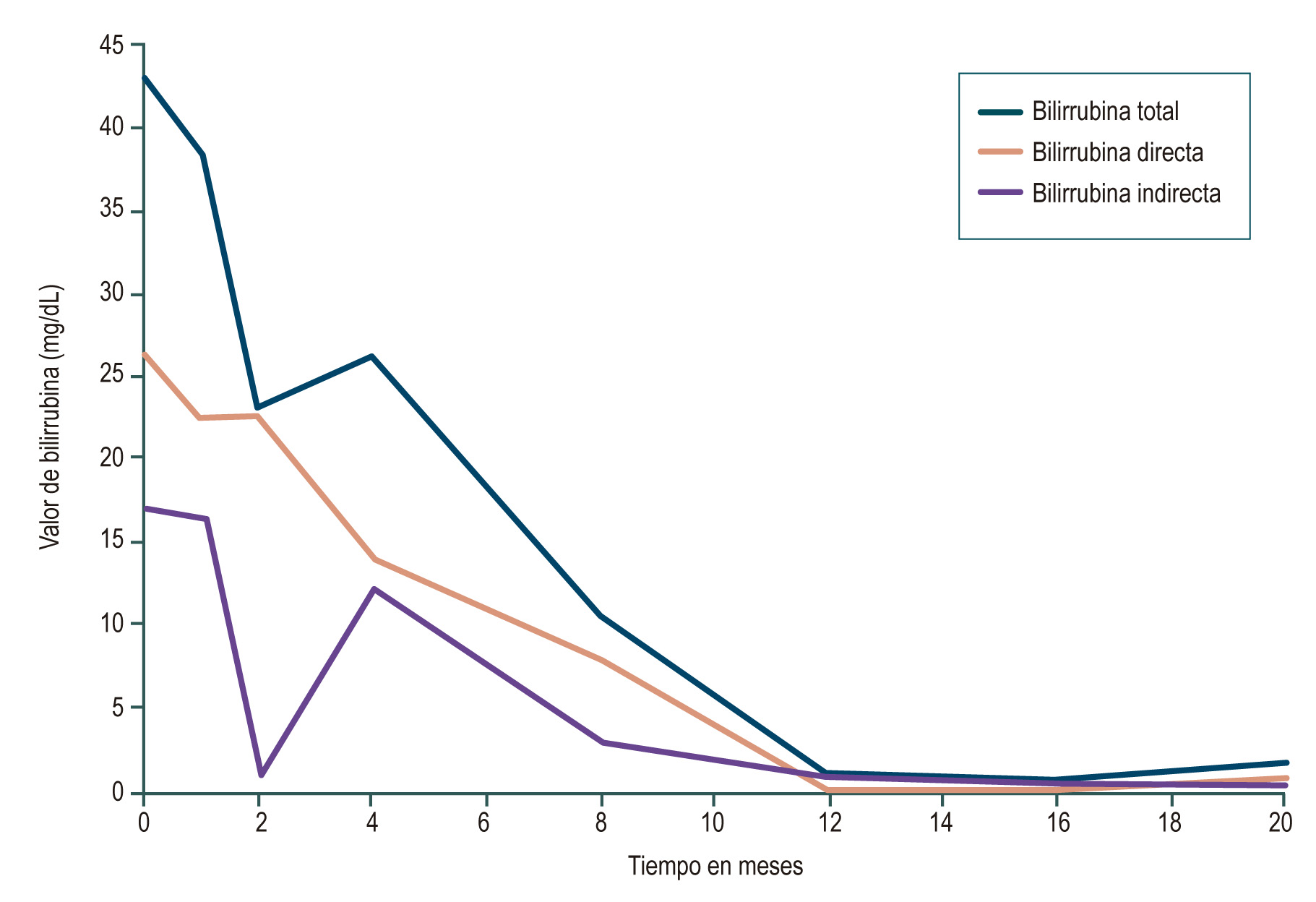
Se presenta el caso de un paciente con virus de la inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH) con colestasis intrahepática grave y con referencia de ictericia recurrente a lo largo de su vida, en el que, luego de varios estudios de colestasis intrahepática, se le diagnosticó CIBR con la mutación del gen ATP8B1 sintomático.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Halawi A, Ibrahim N, Bitar R. Triggers of benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and its pathophysiology: a review of literature. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2021;84(3):477-86. https://doi.org/10.51821/84.3.013
van der Woerd WL, van Mil SWC, Stapelbroek JM, Klomp LWJ, van de Graaf SFJ, Houwen RHJ. Familial cholestasis: Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis, benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24(5):541-53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.010
Gunaydin M, Bozkurter Cil AT. Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: diagnosis, management, and treatment. Hepat Med. 2018;10:95-104. https://doi.org/10.2147/HMER.S137209
Felzen A, Verkade HJ. The spectrum of Progressive Familial Intrahepatic Cholestasis diseases: Update on pathophysiology and emerging treatments. Eur J Med Genet. 2021;64(11):104317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2021.104317
van Wessel DBE, Thompson RJ, Gonzales E, Jankowska I, Shneider BL, Sokal E, et al. Impact of Genotype, Serum Bile Acids, and Surgical Biliary Diversion on Native Liver Survival in FIC1 Deficiency. Hepatology. 2021;74(2):892-906. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.31787
Folvik G, Hilde O, Helge GO. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: review and long-term follow-up of five cases. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2012;47(4):482-8. https://doi.org/10.3109/00365521.2011.650191
De Vloo C, Nevens F. Cholestatic pruritus: an update. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2019;82(1):75-82.
Van Berge Henegouwen GP. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis and Byler’s disease: one gene, two diseases? J Hepatol. 1996;25(3):395-7. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(96)80128-0
van Ooteghem NAM, Klomp LWJ, van Berge-Henegouwen GP, Houwen RHJ. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis progressing to progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis: low GGT cholestasis is a clinical continuum. J Hepatol. 2002;36(3):439-43. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-8278(01)00299-9
van Mil SW, Klomp LW, Bull LN, Houwen RH. FIC1 Disease: A Spectrum of Intrahepatic Cholestatic Disorders. Semin Liver Dis. 2001;21(04):535-44. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2001-19034
Amirneni S, Haep N, Gad MA, Soto-Gutierrez A, Squires JE, Florentino RM. Molecular overview of progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis. World J Gastroenterol. 2020;26(47):7470-84. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i47.7470
Andersen JP, Vestergaard AL, Mikkelsen SA, Mogensen LS, Chalat M, Molday RS. P4-ATPases as Phospholipid Flippases-Structure, Function, and Enigmas. Front Physiol. 2016;7:275. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2016.00275
Luketic VA, Shiffman ML. Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis. Clin Liver Dis. 2004;8(1):133-149. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1089-3261(03)00133-8
Crosigani A, Podda M, Bertolini E, Battezzati PM, Zuin M, Setchell KDR. Failure of ursodeoxycholic acid to prevent a cholestatic episode in a patient with benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis: A study of bile acid metabolism. Hepatology. 1991;13(6):1076-83. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.1840130612
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


















