Dupilumab in Eosinophilic Esophagitis Refractory to Conventional Management in Pediatrics: Report of Two Cases
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1015Keywords:
Eosinophilic esophagitis, dupilumab, anti-interleukin-4, receptor alpha monoclonal antibody, pediatrics, allergyAbstract
Introduction: This publication aims to show the clinical, endoscopic, and histological responses of two pediatric patients who received dupilumab as a management strategy for eosinophilic esophagitis. Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the alpha chain of the interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 receptors involved in the Th2 inflammatory response. The potential therapeutic role of this biological drug has been demonstrated in pediatric clinical trials in other allergic pathologies, such as atopic dermatitis and asthma, with an adequate safety and effectiveness profile.
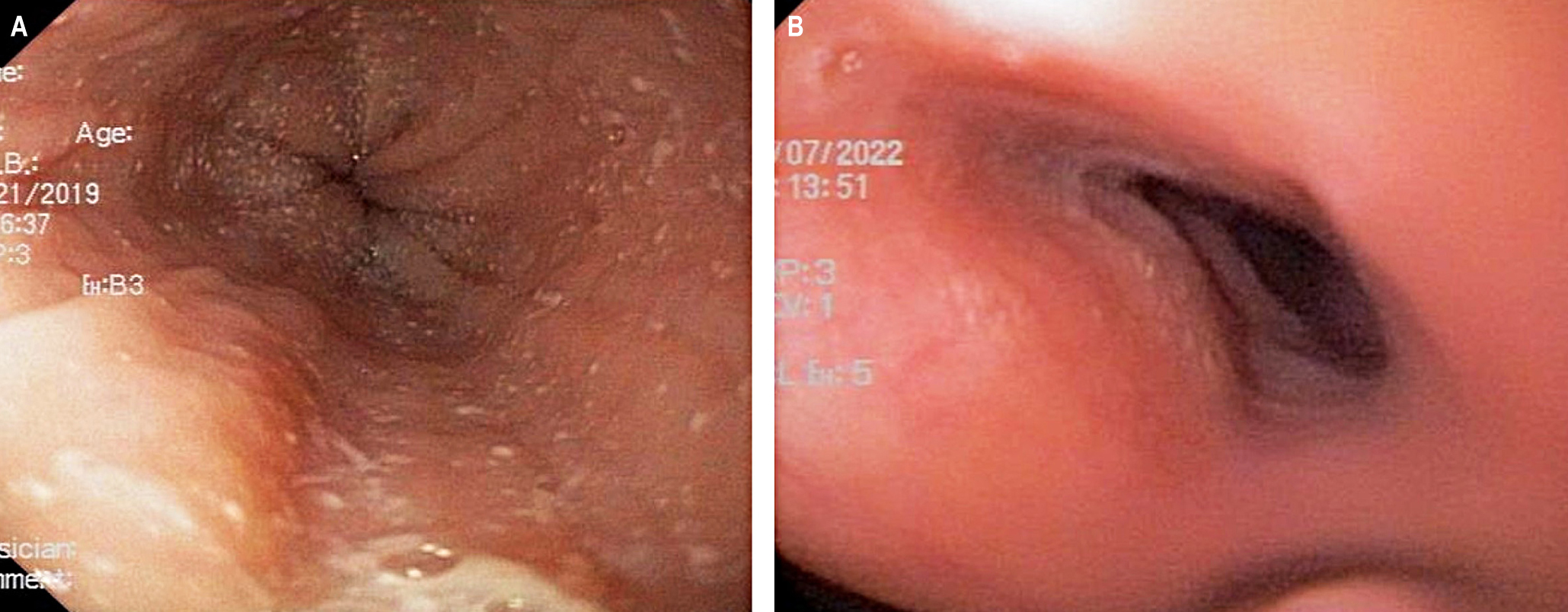
Clinical cases: Two children with a personal history of atopy, allergic rhinitis, asthma, atopic dermatitis, and food allergy began with gastrointestinal symptoms that confirmed the diagnosis of eosinophilic esophagitis. Despite the different management strategies, adequate control of the disease was not achieved, and it is considered that they benefited from management with dupilumab due to the disease evolution and the coexistence of uncontrolled atopic dermatitis.
Conclusions: In recent years, various management strategies in pediatrics have been published, particularly high-dose proton pump inhibitors, topical corticosteroids, and elimination diets. However, despite these strategies, at least one-third of patients may fail to achieve remission with initial treatment, making this entity a therapeutic challenge for the gastroenterologist and pediatric allergist. Our patients received the dose recommended for their weight and age and approved for asthma and atopic dermatitis, resulting in clinical and histological remission. The improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms was accompanied by better control of asthma, rhinitis, and dermatitis. None of the patients had adverse effects of the medication.
Downloads
References
Lucendo AJ, Molina-Infante J, Arias Á, von Arnim U, Bredenoord AJ, Bussmann C, et al. Guidelines on eosinophilic esophagitis: evidence-based statements and recommendations for diagnosis and management in children and adults. Vol. 5, United European Gastroenterology Journal. SAGE Publications Ltd; 2017. p. 335-58. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050640616689525
Furuta GT, Katzka DA. Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Ingelfinger JR, editor. N Engl J Med [Internet]. 2015 Oct 22;373(17):1640-8. Available from: http://www.nejm.org/doi/10.1056/NEJMra1502863 https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra1502863
Gutiérrez Junquera C, Fernández Fernández S, Domínguez-Ortega G, Vila Miravet V, García Puig R, García Romero R, et al. Recommendations for the diagnosis and practical management of paediatric eosinophilic oesophagitis. An Pediatr. 2020 Jun 1;92(6):376.e1-376.e10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anpede.2020.04.005
Dhar A, Haboubi HN, Attwood SE, Auth MKH, Dunn JM, Sweis R, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) and British Society of Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (BSPGHAN) joint consensus guidelines on the diagnosis and management of eosinophilic oesophagitis in children and adults. Gut. 2022 May 23;gutjnl-2022-327326. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327326
O'Shea KM, Aceves SS, Dellon ES, Gupta SK, Spergel JM, Furuta GT, et al. Pathophysiology of Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jan 1;154(2):333-45. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.06.065
Patel N, Goyal A, Thaker A, Troendle D, Parrish C. A Case Series on the Use of Dupilumab for Treatment of Refractory Eosinophilic Gastrointestinal Disorders. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr [Internet]. 2022 Aug 6;75(2):192-5. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003512 https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003512
Gómez-Aldana A, Jaramillo-Santos M, Delgado A, Jaramillo C, Lúquez-Mindiola A. Eosinophilic esophagitis- Current concepts in diagnosis and treatment 2019. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(32):4598-613. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i32.4598
Hamilton JD, Harel S, Swanson BN, Brian W, Chen Z, Rice MS, et al. Dupilumab suppresses type 2 inflammatory biomarkers across multiple atopic, allergic diseases. Clin Exp Allergy. 2021 Jul 1;51(7):915-31. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.13954
Harb H, Chatila TA. Mechanisms of Dupilumab. Vol. 50, Clinical and Experimental Allergy. Blackwell Publishing Ltd; 2020. p. 5-14. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.13491
Pelaia C, Pelaia G, Crimi C, Maglio A, Armentaro G, Calabrese C, et al. Biological Therapy of Severe Asthma with Dupilumab, a Dual Receptor Antagonist of Interleukins 4 and 13. Vaccines. 2022 Jun 19;10(6):974. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10060974
Hirano I, Dellon ES, Hamilton JD, Collins MH, Peterson K, Chehade M, et al. Efficacy of Dupilumab in a Phase 2 Randomized Trial of Adults With Active Eosinophilic Esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 2020 Jan 1;158(1):111-122.e10. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2019.09.042
Licari A, Castagnoli R, Marseglia A, Olivero F, Votto M, Ciprandi G, et al. Dupilumab to Treat Type 2 Inflammatory Diseases in Children and Adolescents. Vol. 22, Pediatric Drugs. Adis; 2020. p. 295-310. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40272-020-00387-2
Amin N, Lim WK, Wipperman MF, Ruddy M, Patel N, Weinreich DR. Dupilumab in Adults and Adolescents with Eosinophilic Esophagitis. 2022;2317-30. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2205982
Spekhorst LS, van der Rijst LP, de Graaf M, van Megen M, Zuithoff NPA, Knulst AC, et al. Dupilumab has a profound effect on specific-IgE levels of several food allergens in atopic dermatitis patients. Allergy Eur J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2022;(February):875-8. https://doi.org/10.1111/all.15591
Rial MJ, Barroso B, Sastre J. Dupilumab for treatment of food allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract [Internet]. 2019;7(2):673-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2018.07.027
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















