Hepatitis C virus reinfection: A review of the topic and case report
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.917Keywords:
Direct-acting antivirals, Hepatitis C Virus, Sustained Virological Response, Reinfection, coinfection VIH/VHCAbstract
Chronic hepatitis C (HCV) infection affects 58 million people and is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. HCV reinfection is a growing problem in people with risk factors such as heavy alcohol use, anal sex, group sex, and sharing needles and syringes. This type of infection is defined as a new HCV infection with a different viral genotype than the first infection in a patient after achieving a sustained viral response (SVR). Reinfection occurs, in part, due to the absence of promotion and prevention strategies. Taking this background into account, more pragmatic approaches have been proposed to control HCV infection and avoid reinfection, such as micro elimination.
This article reports the case of a patient with alterations in biochemical liver markers, for which a diagnostic test for HCV infection and then viral genotyping was requested. Infection by HCV genotype 1, subgenotype 1A, was evidenced. Management with direct-acting antivirals was started, and an adequate SVR12 was documented. Three months later, the patient returned, and the control tests showed a high HCV viral load, for which genotyping was requested, showing a new HCV genotype 4 infection.
Downloads
References
Hepatitis C [Internet]. WHO [citado el 14 de noviembre de 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c
Stanaway JD, Flaxman AD, Naghavi M, Fitzmaurice C, Vos T, Abubakar I, et al. The global burden of viral hepatitis from 1990 to 2013: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013. Lancet. 2016;388(10049):1081-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)30579-7
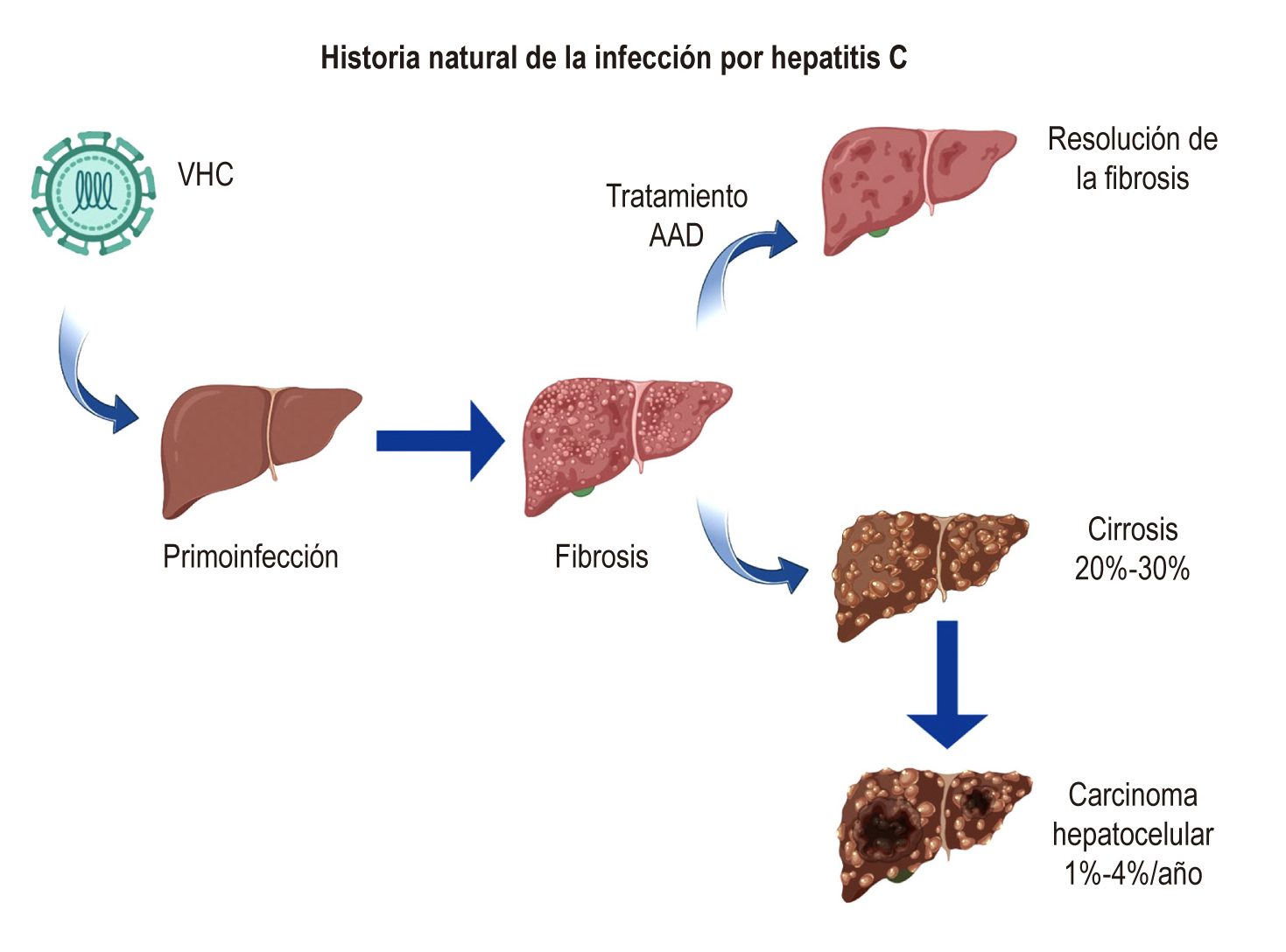
Lingala S, Ghany MG. Natural History of Hepatitis C. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2015;44(4):717-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gtc.2015.07.003
Singal AK, Satapathy SK, Reau N, Wong R, Kuo YF. Hepatitis C remains leading indication for listings and receipt of liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2020;52(1):98-101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2019.08.022
Toniutto P, Bitetto D, Fornasiere E, Fumolo E. Challenges and future developments in liver transplantation. Minerva Gastroenterol Dietol. 2018;65(2):136-52. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1121-421X.18.02529-1
Durand F, Francoz C. The future of liver transplantation for viral hepatitis. Liver Int [Internet]. 2017;37 Suppl 1:130-5. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13310
Global health sector strategy on viral hepatitis 2016-2021. Towards ending viral hepatitis [Internet]. WHO; 2016 [citado el 14 de noviembre de 2021]. Disponible en: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/246177
Falade-Nwulia O, Sulkowski MS, Merkow A, Latkin C, Mehta SH. Understanding and addressing hepatitis C reinfection in the oral direct acting antiviral era. J Viral Hepat. 2018;25(3):220-227. https://doi.org/10.1111/jvh.12859
Mahale P, Engels EA, Li R, Torres HA, Hwang LY, Brown EL, et al. The effect of sustained virological response on the risk of extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C virus infection. Gut. 2018;67(3):553-561. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2017-313983
Li DK, Chung RT. Overview of direct-acting antiviral drugs and drug resistance of hepatitis C virus. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1911:3-32. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8976-8_1
Asselah T, Boyer N, Saadoun D, Martinot-Peignoux M, Marcellin P. Direct-acting antivirals for the treatment of hepatitis C virus infection: optimizing current IFN-free treatment and future perspectives. Liver Int. 2016;36 Suppl 1:47-57. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13027
Manns MP, Buti M, Gane E, Pawlotsky JM, Razavi H, Terrault N, et al. Hepatitis C virus infection. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2017;3:17006. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.6
Manns MP, von Hahn T. Novel therapies for hepatitis C - one pill fits all? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2013;12(8):595-610. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd4050
Pawlotsky JM, Negro F, Aghemo A, Berenguer M, Dalgard O, Dusheiko G, et al. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2018. J Hepatol. 2018;69(2):461-511. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.03.026
Tsukiyama-Kohara K, Kohara M. Molecular Sciences Hepatitis C Virus: Viral Quasispecies and Genotypes. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;19(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010023
Minosse C, Gruber CEM, Rueca M, Taibi C, Zaccarelli M, Grilli E, et al. Late Relapse and Reinfection in HCV Patients Treated with Direct-Acting Antiviral (DAA) Drugs. Viruses. 2021;13(6):1151. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13061151
Sarrazin C, Isakov V, Svarovskaia ES, Hedskog C, Martin R, Chodavarapu K, et al. Late Relapse Versus Hepatitis C Virus Reinfection in Patients With Sustained Virologic Response After Sofosbuvir-Based Therapies. Clin Infect Dis. 2017;64(1):44-52. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciw676
Navas MC, Fuchs A, Schvoerer E, Bohbot A, Aubertin AM, Stoll-Keller F. Dendritic cell susceptibility to hepatitis C virus genotype 1 infection. J Med Virol. 2002;67(2):152-61. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmv.2204
di Lello FA, Culasso ACA, Parodi C, Baré P, Campos RH, García G. New evidence of replication of hepatitis C virus in short-term peripheral blood mononuclear cell cultures. Virus Res. 2014;191(1):1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2014.07.020
Russelli G, Pizzillo P, Iannolo G, Barbera F, Tuzzolino F, Liotta R, et al. HCV replication in gastrointestinal mucosa: Potential extra-hepatic viral reservoir and possible role in HCV infection recurrence after liver transplantation. PLoS One. 2017;12(7):e0181683. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181683
Kemming J, Thimme R, Neumann-Haefelin C. Adaptive Immune Response against Hepatitis C Virus. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5644. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165644
Rehermann B, Thimme R. Insights From Antiviral Therapy Into Immune Responses to Hepatitis B and C Virus Infection. Gastroenterology. 2019;156(2):369-383. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.061
Neumann-Haefelin C, Thimme R. Adaptive immune responses in hepatitis C virus infection. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2013;369:243-62. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-27340-7_10
Muller A, Vlahov D, Akiyama MJ, Kurth A. Hepatitis C Reinfection in People Who Inject Drugs in Resource-Limited Countries: A Systematic Review and Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(14):4951. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17144951
Simmons B, Saleem J, Hill A, Riley RD, Cooke GS. Clinical Infectious Diseases Risk of Late Relapse or Reinfection With Hepatitis C Virus After Achieving a Sustained Virological Response: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2016;62(6):683-694. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/civ948
Mohd Hanafiah K, Groeger J, Flaxman AD, Wiersma ST. Global epidemiology of hepatitis C virus infection: new estimates of age-specific antibody to HCV seroprevalence. Hepatology. 2013;57(4):1333-42. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26141
European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Recommendations on Treatment of Hepatitis C 2016. J Hepatol. 2017;66(1):153-94. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2016.09.001
Chung RT, Davis GL, Jensen DM, Masur H, Saag MS, Thomas DL, et al. Hepatitis C guidance: AASLD-IDSA recommendations for testing, managing, and treating adults infected with hepatitis C virus. Hepatology. 2015;62(3):932-54. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27950
Lok AS, Gardiner DF, Lawitz E, Martorell C, Everson GT, Ghalib R, et al. Preliminary Study of Two Antiviral Agents for Hepatitis C Genotype 1. New England Journal of Medicine. 2012;366(3):216-24. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1104430
Choo QL, Kuo G, Weiner AJ, Overby LR, Bradley DW, Houghton M. Isolation of a cDNA clone derived from a blood-borne non-A, non-B viral hepatitis genome. Science. 1989;244(4902):359-62. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.2523562
Borgia SM, Hedskog C, Parhy B, Hyland RH, Stamm LM, Brainard DM, et al. Identification of a Novel Hepatitis C Virus Genotype From Punjab, India: Expanding Classification of Hepatitis C Virus Into 8 Genotypes. J Infect Dis. 2018;218(11):1722-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiy401
Hedskog C, Parhy B, Chang S, Zeuzem S, Moreno C, Shafran SD, et al. Identification of 19 Novel Hepatitis C Virus Subtypes-Further Expanding HCV Classification. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2019;6(3):ofz076. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofz076
Lanini S, Easterbrook PJ, Zumla A, Ippolito G. Hepatitis C: global epidemiology and strategies for control. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22(10):833-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2016.07.035
Cooke GS, Andrieux-Meyer I, Applegate TL, Atun R, Burry JR, Cheinquer H, et al. Accelerating the elimination of viral hepatitis: a Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Commission. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019;4(2):135-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(18)30270-X
Jin F, Matthews G v., Grulich AE. Sexual transmission of hepatitis C virus among gay and bisexual men: a systematic review. Sex Health. 2017;14(1):28-41. https://doi.org/10.1071/SH16141
Daskalopoulou M, Rodger A, Thornton A, Phillips A, Sherr L, Gilson R, et al. Sexual behaviour, recreational drug use and hepatitis C co-infection in HIV-diagnosed men who have sex with men in the United Kingdom: results from the ASTRA study. J Int AIDS Soc. 2014;17(4 Suppl 3):19630. https://doi.org/10.7448/IAS.17.4.19630
Jordan AE, Perlman DC, Neurer J, Smith DJ, des Jarlais DC, Hagan H. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection among HIV+ men who have sex with men: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J STD AIDS. 2017;28(2):145-59. https://doi.org/10.1177/0956462416630910
Knick T, Sherbuk JE, Dillingham R. Knowledge of Hepatitis C Risk Factors is Lower in High Incidence Regions. J Community Health. 2019;44(1):12-5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10900-018-0545-6
Ingiliz P, Wehmeyer MH, Boesecke C, zur Wiesch JS, Schewe K, Lutz T, et al. Reinfection With the Hepatitis C Virus in Men Who Have Sex With Men After Successful Treatment With Direct-acting Antivirals in Germany: Current Incidence Rates, Compared With Rates During the Interferon Era. Clin Infect Dis. 2020;71(5):1248-54. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciz949
Berenguer J, Gil-Martin Á, Jarrin I, Montes ML, Domínguez L, Aldámiz-Echevarría T, et al. Reinfection by hepatitis C virus following effective all-oral direct-acting antiviral drug therapy in HIV/hepatitis C virus coinfected individuals. AIDS. 2019;33(4):685-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000002103
Smit C, Boyd A, Rijnders BJA, van de Laar TJW, Leyten EM, Bierman WF, et al. HCV micro-elimination in individuals with HIV in the Netherlands 4 years after universal access to direct-acting antivirals: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet HIV. 2021;8(2):e96-105. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30301-5
Boender TS, Smit C, van Sighem A, Bezemer D, Ester CJ, Zaheri S, et al. AIDS Therapy Evaluation in the Netherlands (ATHENA) national observational HIV cohort: cohort profile. BMJ Open. 2018;8(9):e022516. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022516
Adu PA, Rossi C, Binka M, Wong S, Wilton J, Wong J, et al. HCV reinfection rates after cure or spontaneous clearance among HIV-infected and uninfected men who have sex with men. Liver International. 2021;41(3):482-93. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.14762
Lazarus JV, Wiktor S, Colombo M, Thursz M. Micro-elimination - A path to global elimination of hepatitis C. J Hepatol. 2017;67(4):665-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2017.06.033
Braun DL, Hampel B, Ledergerber B, Grube C, Nguyen H, Künzler-Heule P, et al. A Treatment-as-Prevention Trial to Eliminate Hepatitis C Among Men Who Have Sex With Men Living With Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) in the Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Clin Infect Dis. 2021;73(7):e2194-202. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa1124
Toyoda H, Yasuda S, Shiota S, Kumada T, Tanaka J. Lack of hepatitis C virus reinfection in lifetime of Japanese general population with previous hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection successfully treated with anti-HCV therapy. J Infect Chemother. 2021;27(11):1674-1675. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiac.2021.08.018
Okamoto H, Sugiyama Y, Okada S, Kurai K, Akahane Y, Sugai Y, et al. Typing hepatitis C virus by polymerase chain reaction with type-specific primers: application to clinical surveys and tracing infectious sources. J Gen Virol. 1992;73(Pt 3):673-9. https://doi.org/10.1099/0022-1317-73-3-673
Vandelli C, Renzo F, Romanò L, Tisminetzky S, de Palma M, Stroffolini T, et al. Lack of evidence of sexual transmission of hepatitis C among monogamous couples: results of a 10-year prospective follow-up study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99(5):855-9. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04150.x
Terrault NA, Dodge JL, Murphy EL, Tavis JE, Kiss A, Levin TR, et al. Sexual transmission of hepatitis C virus among monogamous heterosexual couples: the HCV partners study. Hepatology. 2013;57(3):881-9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.26164
Carson JM, Hajarizadeh B, Hanson J, O’Beirne J, Iser D, Read P, et al. Effectiveness of treatment for hepatitis C virus reinfection following direct acting antiviral therapy in the REACH-C cohort. Int J Drug Policy. 2021;96:103422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drugpo.2021.103422
Situación de la hepatitis C crónica en los regímenes subsidiado y contributivo de Colombia. Bogotá D. C.: Fondo Colombiano de Enfermedades de Alto Costo, Cuenta de Alto Costo (CAC); 2021.
American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, Infectious Diseases Society of America. Simplified HCV treatment algorithm for treatment-naive adults with compensated cirrhosis [Internet]. [citado el 26 de septiembre de 2021]. Disponible en: https://www.hcvguidelines.org/treatment-naive/simplified-treatment-compensated-cirrhosis Google Scholar
Antiviral resistance testing in the management of hepatitis C virus infection [Internet]. Public Health England; 2018 [citado el 8 de Agosto de 2022]. Disponible en: https://assets.publishing.service.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/1110853/Antiviral_resistance_testing_in_the_management_of_hepatitis_C_virus_infection.pdf
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















