Características clínicas, evolución y desenlaces de pacientes con enfermedad de Crohn atendidos en un hospital de referencia en Colombia: análisis longitudinal sobre una serie de casos
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1260Palabras clave:
Enfermedad de Crohn, Terapia biológica, RemisiónResumen
Objetivo: describir los desenlaces clínicos a dos años de un programa de atención de enfermedad de Crohn (EC) en un hospital de referencia en Colombia.
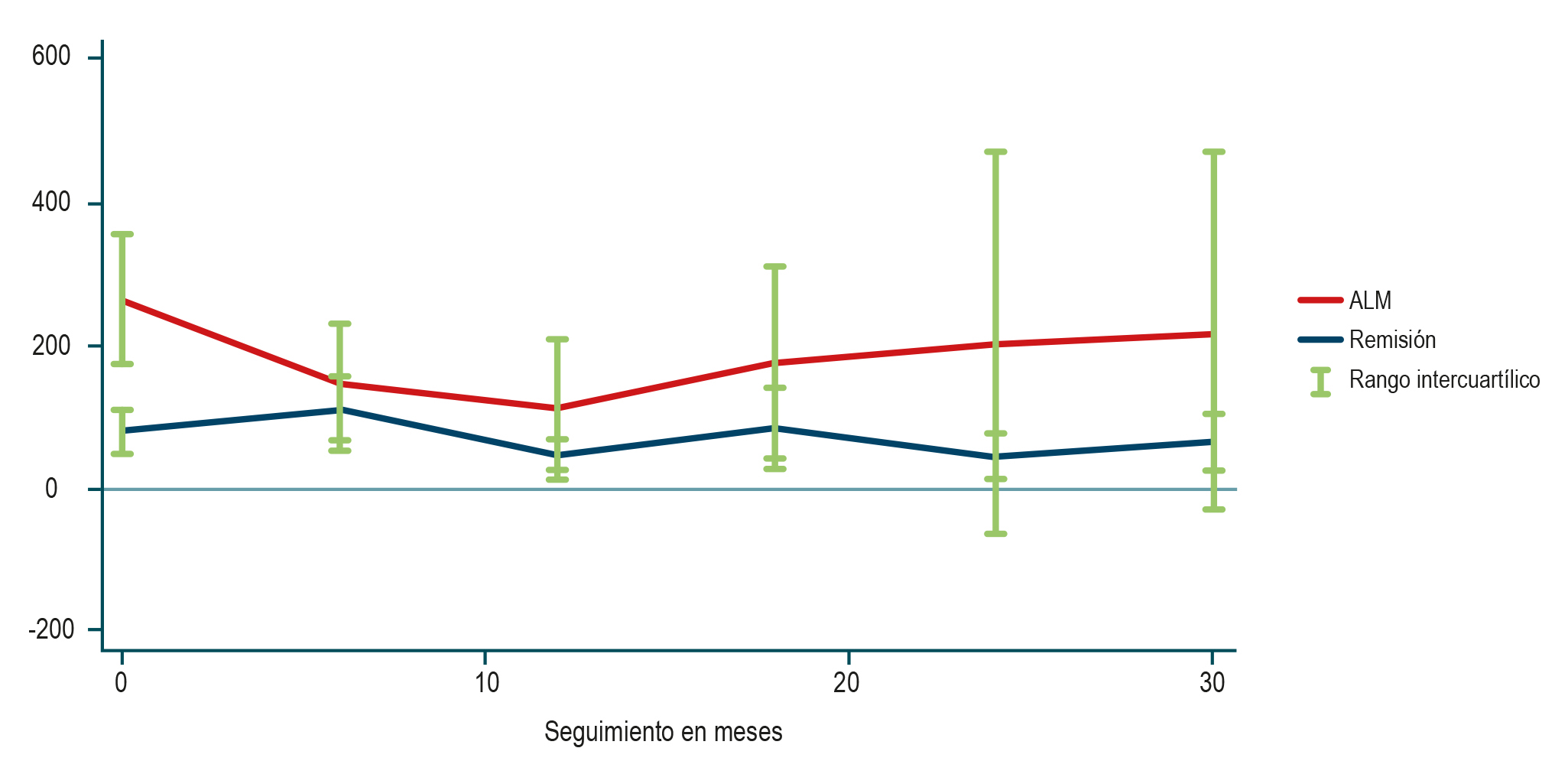
Materiales y métodos: estudio longitudinal basado en una serie de casos de pacientes atendidos por un programa especializado en EC en Colombia entre 2013 y 2023. Se presentan las características clínicas, la actividad al momento del ingreso al programa (Crohn Disease Activity Index [CDAI]), los ajustes al tratamiento y los cambios del CDAI en controles subsecuentes (6, 12, 18, 24 y 30 meses).
Resultados: se incluyeron 22 pacientes con una mediana de edad de 44 años (rango intercuartílico [RIC]: 32-64), 10 (45%) eran hombres, 14 (63,4%) se encontraban en remisión y 8 (36,6%) se encontraban en actividad leve a moderada al ingresar al programa. La mediana de CDAI al ingreso fue de 124 (RIC: 52,7-211,2) con un descenso significativo de los controles realizados a los 12 (CDAI: 50, RIC: 10-115) y 24 meses (CDAI: 24, RIC: 10-117) respectivamente (p < 0,05). Al final del seguimiento, 12 pacientes (80%) se encontraban en remisión, 3 (20%) en actividad leve a moderada, 7 (31,8%) no tuvieron seguimiento a los 2 años y 14 (93,3%) se encontraban en manejo biológico al final del seguimiento.
Conclusión: este estudio presenta las características clínicas, conductas terapéuticas y desenlaces de un programa especializado de atención en EC. Los resultados sugieren que este programa logra una reducción de la actividad de la EC posiblemente debido al uso de terapia biológica. Estudios futuros deberán confirmar los potenciales beneficios de la atención por programas especializados.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Crohn’s disease. The Lancet. 2017;389(10080):1741-55. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31711-1
Kruis W, Katalinic A, Klugmann T, Franke GR, Weismüller J, Leifeld L, et al. Predictive factors for an uncomplicated long-term course of Crohn’s disease: A retrospective analysis. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(7):e263-70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2012.10.012
Van Der Valk ME, Mangen MJJ, Leenders M, Dijkstra G, Van Bodegraven AA, Fidder HH, et al. Healthcare costs of inflammatory bowel disease have shifted from hospitalisation and surgery towards anti-TNFα therapy: Results from the COIN study. Gut. 2014;63(1):72-9. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303376
Singh S, Proctor D, Scott FI, Falck-Ytter Y, Feuerstein JD. AGA Technical Review on the Medical Management of Moderate to Severe Luminal and Perianal Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology. 2021;160(7):2512-2556.e9. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.04.023
Solberg IC, Vatn MH, Høie O, Stray N, Sauar J, Jahnsen J, et al. Clinical Course in Crohn’s Disease: Results of a Norwegian Population-Based Ten-Year Follow-Up Study. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2007;5(12):1430-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2007.09.002
Harvey RF, Bradshaw JM. A simple index of crohn’s-disease activity. The Lancet. 1980;315(8167):514. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(80)92767-1
Hanauer S. Oral pentasa in the treatment of active Crohn?s disease: A meta-analysis of double-blind, placebo-controlled trials. Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology. 2004;2(5):379-88. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00122-3
Suzuki Y, Motoya S, Takazoe M, Kosaka T, Date M, Nii M, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of oral budesonide in Japanese patients with active Crohn’s disease: A multicentre, double-blind, randomized, parallel-group Phase II study. J Crohns Colitis. 2013;7(3):239-47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2012.06.006
Candy S, Wright J, Gerber M, Adams G, Gerig M, Goodman R. A controlled double blind study of azathioprine in the management of Crohn’s disease. Gut. 1995;37(5):674-8. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.37.5.674
Reinisch W, Panés J, Lémann M, Schreiber S, Feagan B, Schmidt S, et al. A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind Trial of Everolimus Versus Azathioprine and Placebo to Maintain Steroid-Induced Remission in Patients With Moderate-to-Severe Active Crohn’s Disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(9):2284-92. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.02024.x
Colombel JF, Sandborn WJ, Reinisch W, Mantzaris GJ, Kornbluth A, Rachmilewitz D, et al. Infliximab, Azathioprine, or Combination Therapy for Crohn’s Disease. New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;362(15):1383-95. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0904492
Singh S, Fumery M, Sandborn WJ, Murad MH. Systematic review and network meta‐analysis: first‐ and second‐line biologic therapies for moderate‐severe Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;48(4):394-409. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14852
Fernández-Ávila DG, Dávila-Ruales V. Frecuencia de uso y costo del tratamiento biológico para enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal y artropatía asociada a enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal en Colombia durante el año 2019. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2014;89(2):213-21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2023.03.007
Juliao-Baños F, Puentes F, López R, Saffon MA, Reyes G, Parra V, et al. Caracterización de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal en Colombia: resultados de un registro nacional. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2021;86(2):153-62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rgmx.2020.05.005
Rojas Rodríguez CA, Sánchez Londoño S, Rojas N, Sepúlveda Copete M, García Abadía JA, Jiménez Rivera DF, et al. Descripción clínico-epidemiológica de pacientes con enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal en una clínica de cuarto nivel en Cali. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2020;35(2):166-73. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.409
García Duperly R, López Panqueva RP, Londoño Schimmer EE, Rey Rubiano AMM, Padron Mercado J, Medellín Abueta AY, et al. Características de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal con respecto a otros centros nacionales de Colombia. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2022;37(1):48-57. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.752
Torres J, Bonovas S, Doherty G, Kucharzik T, Gisbert JP, Raine T, et al. ECCO Guidelines on Therapeutics in Crohn’s Disease: Medical Treatment. J Crohns Colitis. 2020;14(1):4-22.
Maaser C, Sturm A, Vavricka SR, Kucharzik T, Fiorino G, Annese V, et al. ECCO-ESGAR Guideline for Diagnostic Assessment in IBD Part 1: Initial diagnosis, monitoring of known IBD, detection of complications. J Crohns Colitis. 2019;13(2):144-64. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjy113
Spekhorst LM, Visschedijk MC, Alberts R, Festen EA, van der Wouden EJ, Dijkstra G, et al. Performance of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel diseases. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(41):15374-81. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i41.15374
Duveau N, Nachury M, Gerard R, Branche J, Maunoury V, Boualit M, et al. Adalimumab dose escalation is effective and well tolerated in Crohn’s disease patients with secondary loss of response to adalimumab. Dig Liver Dis. 2017;49(2):163-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2016.11.002
Hendler SA, Cohen BL, Colombel JF, Sands BE, Mayer L, Agarwal S. High-Dose Infliximab Therapy in Crohn’s Disease: Clinical Experience, Safety, and Efficacy. J Crohns Colitis. 2015;9(3):266-75. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jju026
Veloso FT. Clinical predictors of Crohn’s disease course. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;28(10):1122-5. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000000698
Oostenbrug LE, van Dullemen HM, Meerman GJ, Jansen PLM, Kleibeuker JH. Clinical outcome of Crohn??s disease according to the Vienna classification: disease location is a useful predictor of disease course. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;18(3):255-61. https://doi.org/10.1097/00042737-200603000-00005
Wolters FL. Phenotype at diagnosis predicts recurrence rates in Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2005;55(8):1124-30. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2005.084061
Schwartz DA, Loftus EV, Tremaine WJ, Panaccione R, Harmsen WS, Zinsmeister AR, et al. The natural history of fistulizing Crohn’s disease in Olmsted County, Minnesota. Gastroenterology. 2002;122(4):875-80. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.32362
Beaugerie L, Seksik P, Nion-Larmurier I, Gendre J, Cosnes J. Predictors of Crohn’s Disease. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(3):650-6. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2005.12.019
Tarrant KM, Barclay ML, Frampton CMA, Gearry RB. Perianal Disease Predicts Changes in Crohn’s Disease Phenotype-Results of a Population-Based Study of Inflammatory Bowel Disease Phenotype. Am J Gastroenterol. 2008;103(12):3082-93. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1572-0241.2008.02212.x
Greenstein AJ, Lachman P, Sachar DB, Springhorn J, Heimann T, Janowitz HD, et al. Perforating and non-perforating indications for repeated operations in Crohn’s disease: evidence for two clinical forms. Gut. 1988;29(5):588-92. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.29.5.588
Selvaratnam S, Gullino S, Shim L, Lee E, Lee A, Paramsothy S, et al. Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel disease in South America: A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 2019;25(47):6866-75. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i47.6866
Yu H, MacIsaac D, Wong JJ, Sellers ZM, Wren AA, Bensen R, et al. Market share and costs of biologic therapies for inflammatory bowel disease in the USA. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018;47(3):364-70. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14430
Peyrin-Biroulet L, Oussalah A, Williet N, Pillot C, Bresler L, Bigard MA. Impact of azathioprine and tumour necrosis factor antagonists on the need for surgery in newly diagnosed Crohn’s disease. Gut. 2011;60(7):930-6. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2010.227884
Vester-Andersen MK, Vind I, Prosberg MV, Bengtsson BG, Blixt T, Munkholm P, et al. Hospitalisation, surgical and medical recurrence rates in inflammatory bowel disease 2003-2011-A Danish population-based cohort study. J Crohns Colitis. 2014;8(12):1675-83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crohns.2014.07.010
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


















