Refractory Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease to Anti-TNF Therapy
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1213Keywords:
Inflammatory bowel disease, pediatrics, Crohn’s diseaseAbstract
Background: Very early-onset inflammatory bowel disease (VEO-IBD), defined as symptom onset before the age of 6 years, presents a significant clinical challenge for healthcare teams. This case report aims to share clinical experience in managing a patient with VEO-IBD.
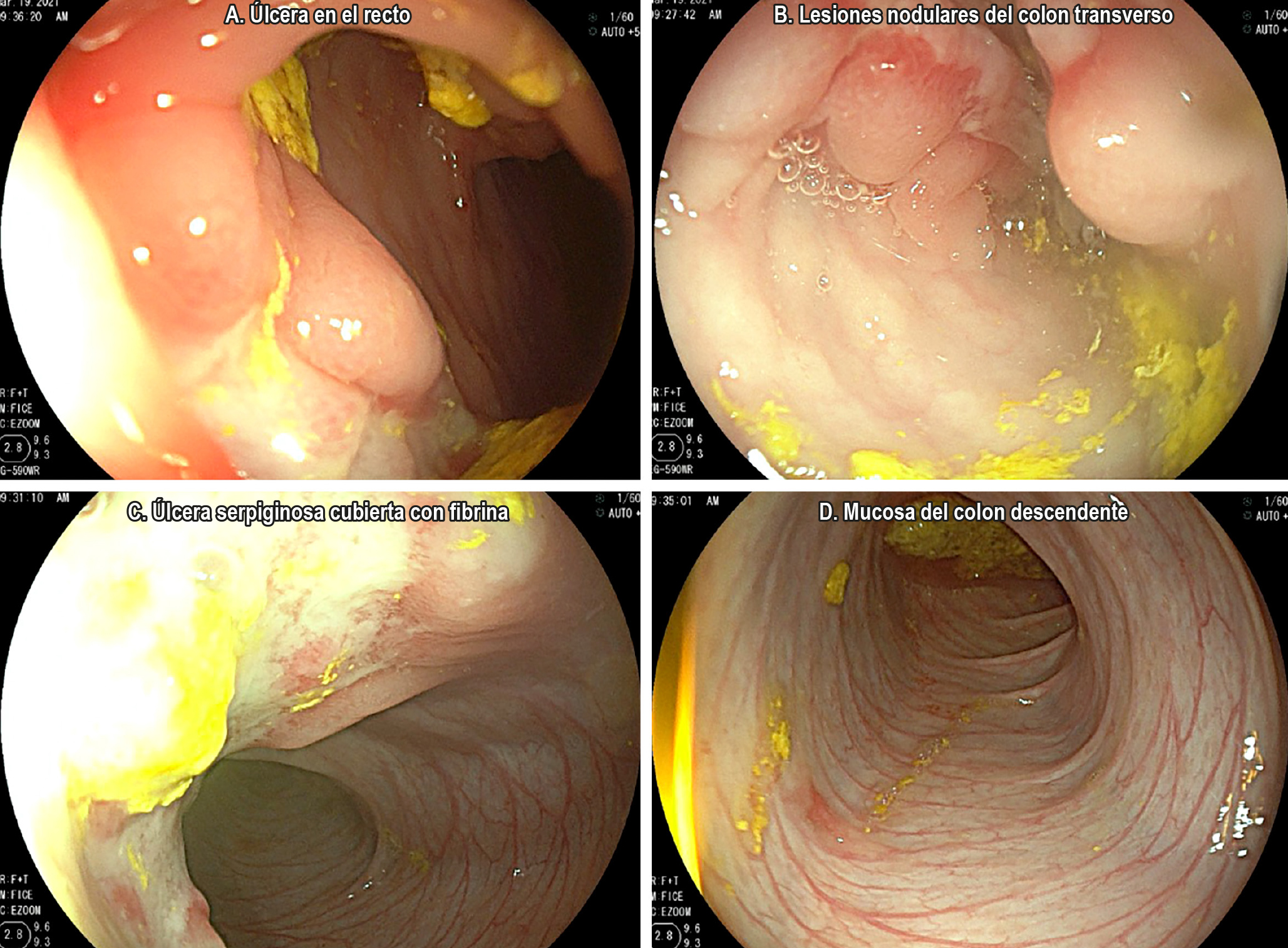
Case Report: We present the case of a 3-year-old boy diagnosed with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn’s disease (CD) phenotype, with disease onset at four months of age. A comprehensive evaluation was conducted to rule out differential diagnoses such as food allergies, immunodeficiencies, and intestinal tuberculosis. Given the early onset, a genetic component was suspected, and genetic testing was performed. The patient presented with pancolitis and perianal involvement and was stratified as high-risk according to the ECCO-ESPGHAN guidelines. After therapeutic failure with infliximab and adalimumab, ustekinumab was initiated with successful clinical remission to date. This therapy has proven effective in refractory pediatric CD cases.
Conclusions: To achieve an accurate diagnosis in suspected pediatric IBD, it is essential to follow clinical practice guidelines and apply individualized diagnostic approaches. Although most VEO-IBD cases have multifactorial etiology, genetic factors may play a significant role, particularly in children under 2 years of age. VEO-IBD is often associated with more severe disease in terms of extent and behavior.
Downloads
References
Kelsen JR, Sullivan KE, Rabizadeh S, Singh N, Snapper S, Elkadri A, et al. North American Society for Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition Position Paper on the Evaluation and Management for Patients with Very Early-onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2020;70(3):389-403. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002567
Cucinotta U, Arrigo S, Dipasquale V, Gramaglia SMC, Laganà F, Romano C, et al. Clinical Course of Very Early-Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023;76(5):590-595. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003730
Parente P, Pastore M, Grillo F, Fassan M, Francalanci P, Dirodi A, et al. Very Early Onset-IBD: evidence for the need of a multidisciplinary approach. Pathologica. 2022;114(1):3-11. https://doi.org/10.32074/1591-951X-336
Krauthammer A, Weintraub I, Shaoul R, Lev-Tzion R, Broide E, Wilschanski M, et al. Infantile-onset inflammatory bowel disease has variable long-term outcomes. Front Pediatr. 2023;11:1097779. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2023.1097779
Uhlig HH, Schwerd T, Koletzko S, Shah N, Kammermeier J, Elkadri A, et al. The diagnostic approach to monogenic very early onset inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2014;147(5):990-1007.e3. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.07.023
Uhlig HH. Monogenic diseases associated with intestinal inflammation: Implications for the understanding of inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 2013;62(12):1795-805. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303956
Kammermeier J, Dziubak R, Pescarin M, Drury S, Godwin H, Reeve K, et al. Phenotypic and genotypic characterisation of inflammatory bowel disease presenting before the age of 2 years. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2017;11(1):60-9. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjw118
Levine A, Koletzko S, Turner D, Escher JC, Cucchiara S, De Ridder L, et al. ESPGHAN revised porto criteria for the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;58(6):795-806. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000000239
Levine A, Griffiths A, Markowitz J, Wilson DC, Turner D, Russell RK, et al. Pediatric modification of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel disease: The Paris classification. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2011;17(6):1314-21. https://doi.org/10.1002/ibd.21493
Singh SK, Srivastava A, Kumari N, Poddar U, Yachha SK, Pandey CM. Differentiation between Crohn disease and intestinal tuberculosis in children. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66(1):e6-11. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001625
Martín De Carpi J, Vila V, Varea V. Aplicación de los criterios de Oporto para el diagnóstico de enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal pediátrica en un centro pediátrico de referencia. An Pediatr. 2011;75(4):232-8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anpedi.2011.03.011
Van Rheenen PF, Aloi M, Assa A, Bronsky J, Escher JC, Fagerberg UL, et al. The Medical Management of Paediatric Crohn’s Disease: An ECCO-ESPGHAN Guideline Update. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2021;15(2):171-94. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjaa161
Vera-Chamorro JF, Sanchez-Franco C, Vargas-Sandoval M, Mora-Quintero DV, Riveros-López JP, Sarmiento-Quintero F, et al. Consenso colombiano de la enfermedad inflamatoria intestinal pediátrica. Rev Colomb Gastroenterol. 2023;38(Supl 1):1-75. https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.943
Akkelle BS, Sengul OK, Volkan B, Tutar E, Ergelen R, Yardimci S, et al. Outcomes of pediatric fistulising perianal Crohn’s disease. Turkish J Gastroenterol. 2021;32(3):240-7. https://doi.org/10.5152/tjg.2021.191034
De Zoeten EF, Pasternak BA, Mattei P, Kramer RE, Kader HA. Diagnosis and treatment of perianal crohn disease: NASPGHAN clinical report and consensus statement. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2013;57(3):401-12. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182a025ee
Amil-Dias J, Kolacek S, Turner D, Pærregaard A, Rintala R, Afzal NA, et al. Surgical Management of Crohn Disease in Children: Guidelines from the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2017;64(5):818-35. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001562
Brückner A, Werkstetter KJ, De Laffolie J, Wendt C, Prell C, Weidenhausen T, et al. Incidence and risk factors for perianal disease in pediatric Crohn disease patients followed in CEDATA-GPGE registry. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2018;66(1):73-8. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000001649
Wetwittayakhlang P, Al Khoury A, Hahn GD, Lakatos PL. The Optimal Management of Fistulizing Crohn’s Disease: Evidence beyond Randomized Clinical Trials. J Clin Med. 2022;11(11):3045. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm11113045
Plevris N, Jenkinson PW, Arnott ID, Jones GR, Lees CW. Higher anti-tumor necrosis factor levels are associated with perianal fistula healing and fistula closure in Crohn’s disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;32(1):32-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MEG.0000000000001561
Yarur AJ, Kanagala V, Stein DJ, Czul F, Quintero MA, Agrawal D, et al. Higher infliximab trough levels are associated with perianal fistula healing in patients with Crohn’s disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2017;45(7):933-40. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.13970
Kerur B, Fiedler K, Stahl M, Hyams J, Stephens M, Lu Y, et al. Utilization of Antitumor Necrosis Factor Biologics in Very Early Onset Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Multicenter Retrospective Cohort Study From North America. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2022;75(1):64-9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003464
Hyams JS, Griffiths A, Markowitz J, Baldassano RN, Faubion WA, Colletti RB, et al. Safety and efficacy of adalimumab for moderate to severe crohn’s disease in children. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(2):365-374.e2. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2012.04.046
Faubion WA, Dubinsky M, Ruemmele FM, Escher J, Rosh J, Hyams JS, et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Adalimumab in Pediatric Patients with Crohn’s Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017;23(3):453-60. https://doi.org/10.1097/MIB.0000000000001021
Kelsen JR, Grossman AB, Pauly-Hubbard H, Gupta K, Baldassano RN, Mamula P. Infliximab therapy in pediatric patients 7 years of age and younger. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2014;59(6):758-62. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000000533
Weintraub Y, Collen Veit L, Hussey S, Mitrova K, Croft NM, Kang B, et al. P570 Efficacy and safety of Adalimumab in Very Early-onset IBD- A Multicentre Study from the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of ESPGHAN. J Crohn’s Colitis. 2024;18(Supplement_1):i1114-5. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjad212.0700
Marsal J, Barreiro-de Acosta M, Blumenstein I, Cappello M, Bazin T, Sebastian S. Management of Non-response and Loss of Response to Anti-tumor Necrosis Factor Therapy in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Front Med. 2022;9:897936. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2022.897936
Gisbert JP, Chaparro M. Ustekinumab to treat Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017;40(10):688-698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastrohep.2017.08.006
Chapuis-Biron C, Kirchgesner J, Pariente B, Bouhnik Y, Amiot A, Viennot S, et al. Ustekinumab for Perianal Crohn’s Disease: The BioLAP Multicenter Study from the GETAID. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115(11):1812-20. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000000810
Dayan JR, Dolinger M, Benkov K, Dunkin D, Jossen J, Lai J, et al. Real World Experience with Ustekinumab in Children and Young Adults at a Tertiary Care Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Disease Center. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2019;69(1):61-7. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000002362
Koudsi M, Martinez-Vinson C, Pigneur B, Willot S, Djamal D, Enaud R, et al. Ustekinumab use in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a French multicenter study from the pediatric GETAID. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2023;76(6):763-770. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPG.0000000000003758
Jin HY, Lim JS, Lee Y, Choi Y, Oh SH, Kim KM, et al. Growth, puberty, and bone health in children and adolescents with inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Pediatr. 2021;21(1):35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-021-02496-4
Downloads
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.



















