Trastornos de la interacción cerebro-intestino (trastornos funcionales digestivos): neuromoduladores en la práctica clínica (parte II)
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.22516/25007440.1133Palabras clave:
Trastornos del sistema digestivo, neurotransmisores, antidepresivosResumen
Introducción: este artículo continúa la revisión de los neuromoduladores utilizados en la práctica clínica y su papel en el tratamiento de los diferentes trastornos de la interacción cerebro-intestino (TICI), en particular los gástricos, intestinales y anales.
Materiales y métodos: el grupo de trabajo revisó las patologías más frecuentes y los medicamentos según la bibliografía más reciente, y de acuerdo con la mejor evidencia clínica en cada caso.
Resultados: debido a la diversidad de trastornos, tipos de estudios y opciones terapéuticas, se decidió presentar aquellas evidencias con los mejores resultados para cada caso, en los que se determinaron las dosis utilizadas, sus resultados y efectos colaterales.
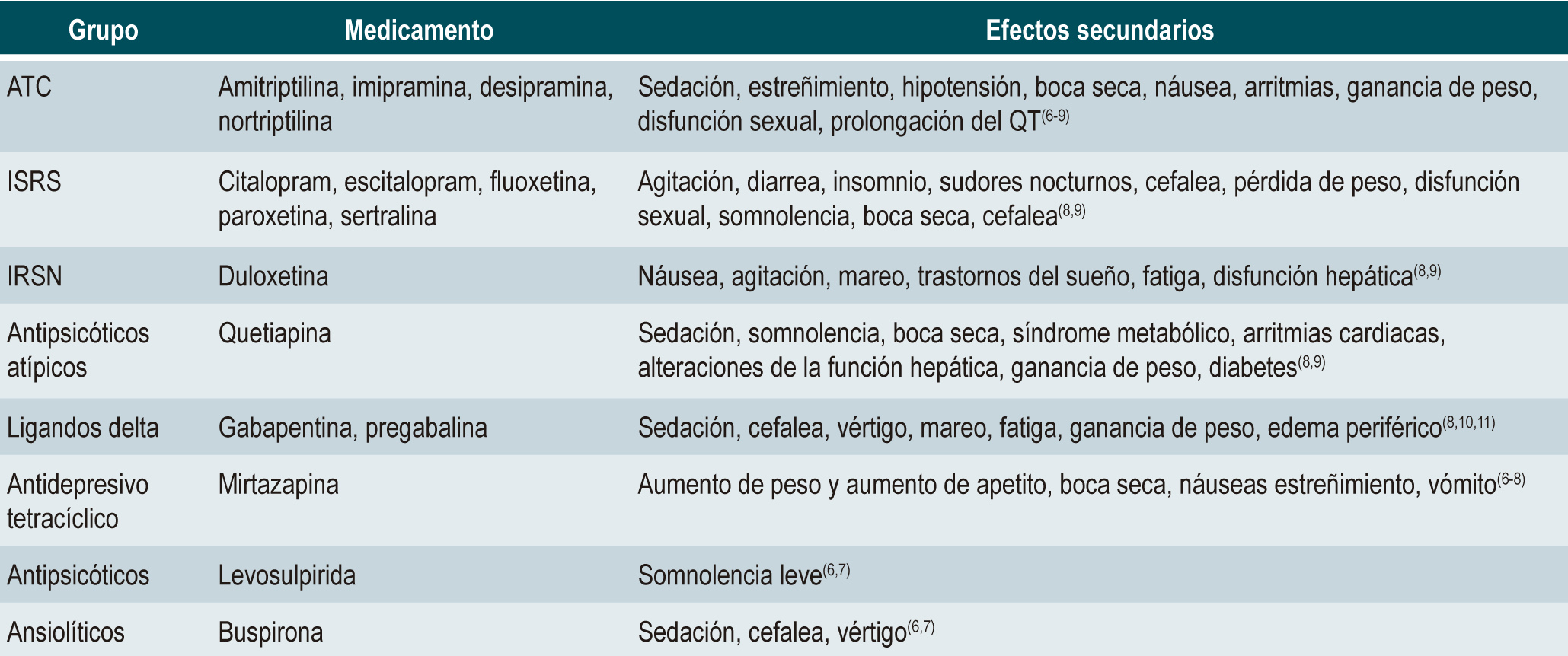
Conclusiones: se presenta la mejor evidencia disponible de los medicamentos utilizados en cada TICI; al finalizar se presenta una tabla en la que se resaltan para cada condición clínica los medicamentos más utilizados, sus dosis y sus efectos gastrointestinales, y en otra tabla, los efectos secundarios más importantes. Dado que la evidencia disponible no resulta definitiva, se requiere para cada condición más ensayos clínicos controlados que puedan confirmar la efectividad y seguridad de estos.
Descargas
Referencias bibliográficas
Koduru P, Irani M, Quigley EMM. Definition, Pathogenesis, and Management of That Cursed Dyspepsia. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;16(4):467-79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2017.09.002
Miwa H, Nagahara A, Asakawa A, Arai M, Oshima T, Kasugai K, et al. Evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for functional dyspepsia 2021. J Gastroenterol. 2022;57(2):47-61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00535-021-01843-7
Stanghellini V, Chan FKL, Hasler WL, Malagelada JR, Suzuki H, Tack J, et al. Gastroduodenal Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1380-92. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.011
Black CJ, Paine PA, Agrawal A, Aziz I, Eugenicos MP, Houghton LA, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the management of functional dyspepsia. Gut. 2022;71(9):1697-723. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327737
Moayyedi PM, Lacy BE, Andrews CN, Enns RA, Howden CW, Vakil N. ACG and CAG Clinical Guideline: Management of Dyspepsia. Am J Gastroenterol. 2017;112(7):988-1013. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2017.154
Bosman L, Wauters L, Vanuytsel T. Neuromodulating agents in functional dyspepsia: a comprehensive review. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2023;86(1):49-57. https://doi.org/10.51821/86.1.10998
Wauters L, Talley NJ, Walker MM, Tack J, Vanuytsel T. Novel concepts in the pathophysiology and treatment of functional dyspepsia. Gut. 2020;69(3):591-600. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2019-318536
Drossman DA, Tack J, Ford AC, Szigethy E, Törnblom H, Van Oudenhove L. Neuromodulators for Functional Gastrointestinal Disorders (Disorders of Gut-Brain Interaction): A Rome Foundation Working Team Report. Gastroenterology. 2018;154(4):1140-1171.e1. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2017.11.279
Younger J, Parkitny L, McLain D. The use of low-dose naltrexone (LDN) as a novel anti-inflammatory treatment for chronic pain. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33(4):451-9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2517-2
Rao SSC, Bharucha AE, Chiarioni G, Felt-Bersma R, Knowles C, Malcolm A, et al. Functional Anorectal Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1430-1442.e4. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.009
Carrington EV, Popa SL, Chiarioni G. Proctalgia Syndromes: Update in Diagnosis and Management. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2020;22(7):35. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-020-00768-0
Engsbro AL, Begtrup LM, Haastrup P, Storsveen MM, Bytzer P, Kjeldsen J, et al. A positive diagnostic strategy is safe and saves endoscopies in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: A five-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021;33(3):e14004. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.14004
Ford AC, Lacy BE, Harris LA, Quigley EMM, Moayyedi P. Effect of Antidepressants and Psychological Therapies in Irritable Bowel Syndrome: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019;114(1):21-39. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5
Kilgallon E, Vasant DH, Green D, Shields PL, Hamdy S, Lal S, et al. Chronic continuous abdominal pain: evaluation of diagnostic features, iatrogenesis and drug treatments in a cohort of 103 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;49(10):1282-92. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.15241
Yang H, Chen H, Hu B. Evaluation of the short-term efficacy of local analgesic (lidocaine) and opioid analgesic (sufentanil) on patients with centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2021;14:17562848211021783. https://doi.org/10.1177/17562848211021783
Zhou W, Li X, Huang Y, Xu X, Liu Y, Wang J, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of psychotropic drugs for functional dyspepsia in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Medicine. 2021;100(20):E26046. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000026046
Lacy BE, Mearin F, Chang L, Chey WD, Lembo AJ, Simren M, et al. Bowel Disorders. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1393-1407.e5. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.031
Vasant DH, Paine PA, Black CJ, Houghton LA, Everitt HA, Corsetti M, et al. British Society of Gastroenterology guidelines on the management of irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2021;70(7):1214-40. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324598
Black CJ, Yuan Y, Selinger CP, Camilleri M, Quigley EMM, Moayyedi P, et al. Efficacy of soluble fibre, antispasmodic drugs, and gut-brain neuromodulators in irritable bowel syndrome: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;5(2):117-31. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30324-3
Black CJ, Staudacher HM, Ford AC. Efficacy of a low FODMAP diet in irritable bowel syndrome: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Gut. 2022;71(6):1117-1126. https://doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2021-325214
Keefer L, Drossman DA, Guthrie E, Simrén M, Tillisch K, Olden K, et al. Centrally Mediated Disorders of Gastrointestinal Pain. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(6):1408-19. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2016.02.034
Grover M, Drossman DA. Functional abdominal pain. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2010;12(5):391-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-010-0125-0
Sperber AD, Drossman DA. Review article: The functional abdominal pain syndrome. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2011;33(5):514-24. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2010.04561.x
Drossman DA. 2012 David Sun lecture: helping your patient by helping yourself--how to improve the patient-physician relationship by optimizing communication skills. Am J Gastroenterol. 2013;108(4):521-8. https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2013.56
Lacy BE, Pimentel M, Brenner DM, Chey WD, Keefer LA, Long MD, et al. ACG Clinical Guideline: Management of Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021;116(1):17-44. https://doi.org/10.14309/ajg.0000000000001036
Tang Y, Song J, Zhu Y, Chen H, Yao W, Zou D. Analysis of clinical characteristics of centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome, exploration of diagnostic markers and its relationship with the efficacy of duloxetine treatment. Medicine. 2022;101(48):E32134. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000032134
Xu R, Wang Y, Han W. Randomized clinical trial: the effects of pregabalin for centrally mediated abdominal pain syndrome. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2023;16:175628482311523. https://doi.org/10.1177/17562848231152334
Descargas
Publicado
Cómo citar
Número
Sección
Licencia
Derechos de autor 2024 Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-SinDerivadas 4.0.
Aquellos autores/as que tengan publicaciones con esta revista, aceptan los términos siguientes:
Los autores/as ceden sus derechos de autor y garantizarán a la revista el derecho de primera publicación de su obra, el cuál estará simultáneamente sujeto a la Licencia de reconocimiento de Creative Commons que permite a terceros compartir la obra siempre que se indique su autor y su primera publicación en esta revista.
Los contenidos están protegidos bajo una licencia de Creative Commons Reconocimiento-NoComercial-SinObraDerivada 4.0 Internacional.


















